dec . 19, 2024 23:55 Back to list
3 4 deep well pump
The Importance of 3% and 4% Deep Well Pumps in Modern Water Supply Systems
Deep well pumps play a crucial role in extracting groundwater, especially in regions where surface water is scarce or unreliable. Among the various types of deep well pumps, 3% and 4% pumps have gained visibility due to their efficiency and effectiveness in bringing up water from significant depths. This article delves into the technology behind these pumps, their applications, and their advantages.
Understanding Deep Well Pumps
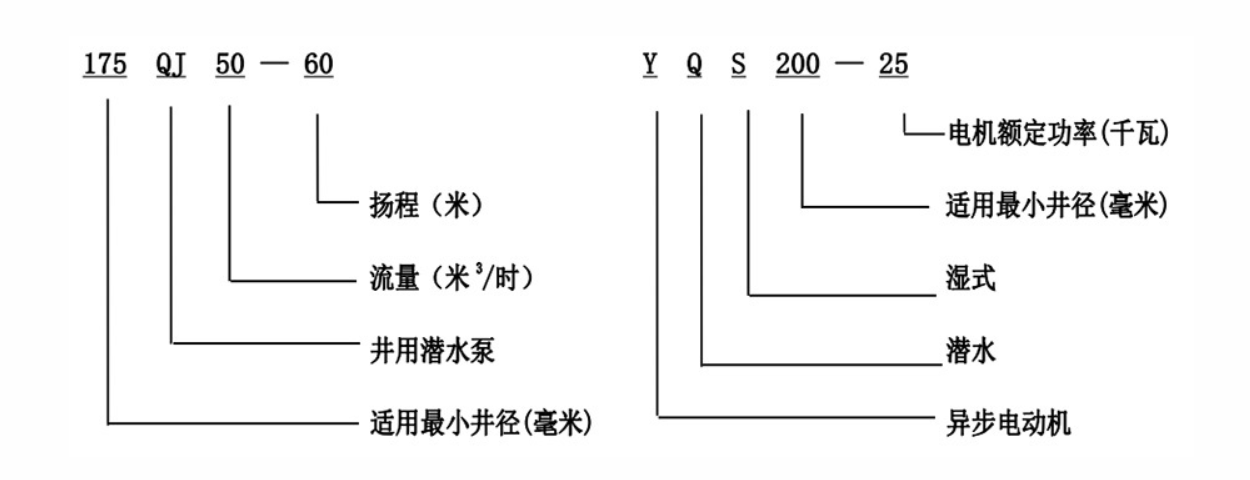
Deep well pumps are designed for wells that have water sources situated below significant depths, often hundreds of feet underground. The primary function of these pumps is to lift water efficiently to the surface, where it can be used for agricultural, industrial, or residential purposes. The percentage notation, like 3% and 4%, typically refers to the energy efficiency and flow rate capabilities of these pumps, indicating their performance metrics under various conditions.
For instance, a 3% deep well pump may refer to a model that can sustain a flow rate while consuming only 3% of the total energy input, showcasing its eco-friendly and economically viable design. Similarly, the 4% model may provide a higher flow rate or increased durability, making it suitable for demanding applications.
Applications of 3% and 4% Deep Well Pumps
1. Agriculture One of the most significant applications of deep well pumps is in agriculture. Farmers rely on these pumps for irrigation, especially in arid regions where rainfall is insufficient. The efficiency of water extraction directly influences crop yield and sustainability, making 3% and 4% pumps vital for modern farming techniques.
2. Municipal Water Supply Many cities and towns depend on deep well pumps to maintain their water supply. As populations grow and surface water sources become depleted, deep well pumps provide an essential alternative. The efficiency levels of 3% and 4% models ensure that municipalities can manage their resources effectively while meeting the demands of their residents.
3 4 deep well pump
3. Industrial Use Industries needing water for manufacturing processes, cooling, or cleaning often turn to deep well pumps. The reliable and efficient operation of 3% and 4% pumps ensures that these sectors maintain productivity while minimizing operational costs.
Advantages of 3% and 4% Deep Well Pumps
1. Energy Efficiency One of the notable advantages of 3% and 4% deep well pumps is their energy efficiency. As energy costs continue to rise, selecting a pump that consumes less power is crucial for reducing operational expenses.
2. Reliability and Durability These pumps are typically built to withstand harsh underground conditions, ensuring long-term reliability. Their ability to operate effectively over extended periods without failure reduces maintenance costs and downtime.
3. Environmentally Friendly The reduced energy consumption of 3% and 4% models also plays a role in lower carbon emissions. By utilizing these pumps, users can contribute to environmental conservation efforts while meeting their water needs.
4. Flexibility and Scalability The adaptability of deep well pumps makes them suitable for various applications, from small farms to large municipal water systems. The ability to scale operations easily ensures that users can adjust to changing demands without significant infrastructure overhauls.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 3% and 4% deep well pumps represent a vital component in modern water management systems. Their efficiency, reliability, and versatility allow for a sustainable approach to water extraction, addressing the needs of agriculture, municipalities, and industries alike. As the demand for clean water continues to grow, the integration of advanced deep well pumping technologies will play an essential role in shaping our water supply infrastructure for the future.
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
