Abe . 05, 2024 15:12 Back to list
submersible utility pumps
Understanding Submersible Utility Pumps Applications and Benefits
Submersible utility pumps are essential tools used across various industries and settings, offering reliable solutions for dewatering, drainage, and various fluid transfer tasks. As the name suggests, these pumps operate underwater, making them particularly effective for applications where other types of pumps might struggle. Understanding the characteristics, applications, and benefits of submersible utility pumps can help users make informed decisions for their specific needs.
What is a Submersible Utility Pump?
A submersible utility pump is a type of pump designed to work while submerged in water or other liquids. Unlike traditional pumps that sit above the liquid they are pumping, these pumps are sealed and equipped with a motor that can operate while completely underwater. This design allows them to push fluids to the surface or transport them to another location effectively. Submersible utility pumps are typically made from durable materials that resist corrosion and wear, making them suitable for a variety of environments, including residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
Common Applications
Submersible utility pumps are widely used for numerous applications. One of the most common uses is for draining flooded basements, where they can quickly remove excess water following rainfall or plumbing failures. Homeowners often rely on these pumps to maintain their properties and protect against water damage.
In construction, submersible utility pumps are integral for dewatering excavations and keeping construction sites dry
. They are capable of handling substantial volumes of water, making them indispensable for large-scale projects. These pumps are also employed in agriculture for irrigation and drainage purposes, allowing farmers to manage water levels in fields effectively.Utility pumps are also useful in municipal applications, such as pumping sewage or wastewater. They help manage stormwater systems, ensuring that excess water is efficiently removed from streets and drainage systems during heavy rain events. Furthermore, these pumps play a crucial role in industrial settings, where they facilitate the transfer of fluids and prevent any potential flooding risks.
submersible utility pumps
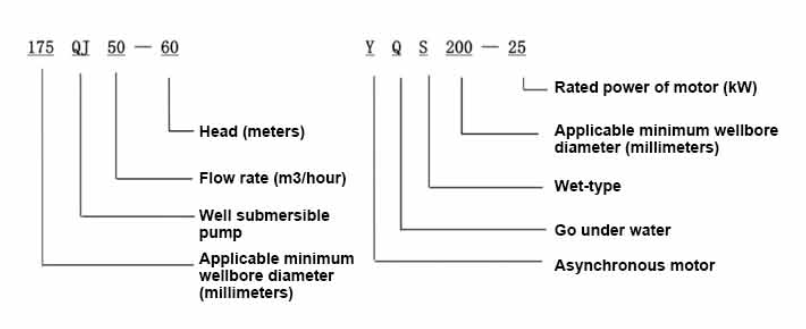
Benefits of Submersible Utility Pumps
The benefits of using submersible utility pumps are numerous. First and foremost, their ability to operate underwater means they are incredibly efficient at managing water and preventing flooding. Their design allows them to push water to greater heights than many other pumps, making them suitable for a variety of vertical lifting applications.
Additionally, submersible pumps are usually compact and portable, enabling ease of transport and installation. Many models come with features that enhance their usability, such as automatic shut-off capabilities when water levels drop, or built-in float switches that allow for hands-free operation.
The energy efficiency of submersible pumps is another significant advantage. Since these pumps work underwater, they require less energy to function compared to some external pump systems. This efficiency can translate into lower utility bills and reduced environmental impact.
Furthermore, these pumps are designed to handle solid particles and debris, making them ideal for dirty water applications. Their robust construction allows them to operate in rugged conditions without the risk of damage, ensuring reliability and longevity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, submersible utility pumps are versatile and effective solutions for a wide range of fluid transfer needs. From residential to industrial applications, their ability to work underwater provides significant advantages in efficiency and functionality. By understanding their features and benefits, users can select the right pump for their specific requirements, ensuring reliable performance and peace of mind. Whether for draining basements, managing stormwater, or supporting construction projects, submersible utility pumps are invaluable tools in effective water management.
-
Water Pumps: Solutions for Every Need
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Submersible Well Pumps: Reliable Water Solutions
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Stainless Steel Water Pumps: Quality and Durability
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Powerful Water Pumps: Your Solution for Efficient Water Management
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Oil vs Water Filled Submersible Pumps: Which is Better?
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Deep Well Pumps: Power and Reliability
NewsJul.30,2025
-
 Water Pumps: Solutions for Every NeedWhen it comes to handling dirty water, the dirty water pump is a must-have.Detail
Water Pumps: Solutions for Every NeedWhen it comes to handling dirty water, the dirty water pump is a must-have.Detail -
 Submersible Well Pumps: Reliable Water SolutionsWhen it comes to ensuring a reliable water supply, submersible well pumps are a top choice.Detail
Submersible Well Pumps: Reliable Water SolutionsWhen it comes to ensuring a reliable water supply, submersible well pumps are a top choice.Detail -
 Stainless Steel Water Pumps: Quality and DurabilityWhen it comes to choosing a water pump, the stainless steel water pump price is a crucial factor.Detail
Stainless Steel Water Pumps: Quality and DurabilityWhen it comes to choosing a water pump, the stainless steel water pump price is a crucial factor.Detail
