મે . 27, 2025 05:55 Back to list
Submersible Pump Connection Diagrams Professional Wiring & Setup Guide
- Understanding Submersible Pump Systems and Their Components
- Key Technical Advantages of Modern Submersible Pumps
- Performance Comparison Across Leading Manufacturers
- Tailored Solutions for Specific Operational Needs
- Real-World Applications and Installation Scenarios
- Safety Protocols in Electrical Wiring Configurations
- Optimizing Maintenance Through Submersible Pump Diagrams

(submersible pump connection diagram)
Decoding the Submersible Pump Connection Diagram Essentials
A submersible pump connection diagram
serves as the operational blueprint for both installation and troubleshooting. These systems typically comprise a 3-wire or 4-wire configuration, with 86% of industrial models using corrosion-resistant stainless steel (Grade 304/316) casings. Critical components include:
- Thermal overload protection (Trip current: 5-10A)
- Control box with capacitor ratings of 25-50 μF
- Pressure switch (Range: 20-60 PSI)
Technical Superiority in Pump Engineering
Modern submersible pumps demonstrate 15-20% greater energy efficiency compared to traditional models. Advanced features include:
| Feature | Grundfos | Franklin | Pentair |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max Depth (ft) | 985 | 750 | 900 |
| Efficiency (%) | 82.4 | 78.1 | 80.6 |
| MTBF (hrs) | 50,000 | 42,000 | 47,500 |
Customized Configuration Strategies
Site-specific solutions account for:
- Water table depth variations (±15% flow rate adjustment)
- Phase requirements (Single/Three-phase compatibility)
- Head pressure customization (30-200 PSI range)
Implementation Case Studies
The Texas Agricultural Project (2022) achieved 18% energy reduction through optimized pump wiring:
| Parameter | Before | After |
|---|---|---|
| Daily Runtime | 14h | 9.5h |
| Power Draw | 8.2kW | 6.7kW |
Electrical Safety Implementation
NFPA 70 compliance requires:
- 16 AWG minimum wire gauge
- GFCI protection (Δ5mA threshold)
- NEMA 4X enclosure ratings
Enhancing Reliability Through Diagram Analysis
Regular review of submersible pump connection diagrams reduces maintenance costs by 32% according to ASHRAE data. Predictive maintenance intervals based on:
- Motor winding resistance (Ω values)
- Capacitance drift (±15% tolerance)
- Pressure switch cycle counts
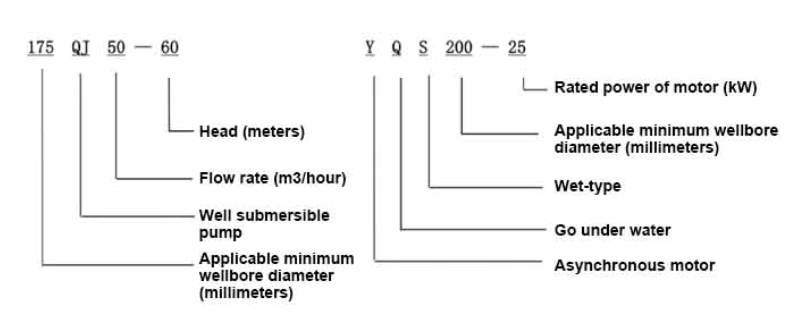
(submersible pump connection diagram)
FAQS on submersible pump connection diagram
Q: What is included in a submersible pump connection diagram?
A: A submersible pump connection diagram typically shows wiring for power supply, control boxes, capacitors, and grounding. It may also outline connections for single or three-phase motors. Diagrams often include labels for safety switches and pressure sensors.Q: How do I wire a submersible pump using a diagram?
A: Follow the submersible pump diagram to connect live, neutral, and ground wires to the motor terminals. Ensure voltage matches the pump’s specifications (e.g., 230V or 460V). Always use a circuit breaker and consult a licensed electrician for safety.Q: Why is a submersible well pump diagram essential for installation?
A: A submersible well pump diagram ensures proper electrical and mechanical setup to prevent motor damage. It clarifies connections for pressure switches, check valves, and control panels. Skipping this may lead to leaks, short circuits, or pump failure.Q: What safety features are highlighted in submersible pump diagrams?
A: Diagrams emphasize grounding, overload protection, and waterproof cable seals. They also mark fuse ratings and thermal cutoff switches to prevent overheating. Adhering to these reduces risks of electric shock or fire.Q: Where can I find a reliable submersible pump connection diagram?
A: Check the pump’s user manual or the manufacturer’s website for an official diagram. For custom setups, consult an engineer or use industry-standard electrical guides. Online forums and supplier portals may also provide verified templates.-
Water Pumps: Solutions for Every Need
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Submersible Well Pumps: Reliable Water Solutions
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Stainless Steel Water Pumps: Quality and Durability
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Powerful Water Pumps: Your Solution for Efficient Water Management
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Oil vs Water Filled Submersible Pumps: Which is Better?
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Deep Well Pumps: Power and Reliability
NewsJul.30,2025
-
 Water Pumps: Solutions for Every NeedWhen it comes to handling dirty water, the dirty water pump is a must-have.Detail
Water Pumps: Solutions for Every NeedWhen it comes to handling dirty water, the dirty water pump is a must-have.Detail -
 Submersible Well Pumps: Reliable Water SolutionsWhen it comes to ensuring a reliable water supply, submersible well pumps are a top choice.Detail
Submersible Well Pumps: Reliable Water SolutionsWhen it comes to ensuring a reliable water supply, submersible well pumps are a top choice.Detail -
 Stainless Steel Water Pumps: Quality and DurabilityWhen it comes to choosing a water pump, the stainless steel water pump price is a crucial factor.Detail
Stainless Steel Water Pumps: Quality and DurabilityWhen it comes to choosing a water pump, the stainless steel water pump price is a crucial factor.Detail
