des . 13, 2024 21:18 Back to list
hydraulic submersible pump
Understanding Hydraulic Submersible Pumps Functionality and Applications
Hydraulic submersible pumps are essential devices designed to perform various tasks in different industries, notably in construction, mining, and wastewater management. These pumps operate effectively underwater, offering a reliable solution for transporting fluids and managing water levels in various applications. This article delves into the functionality, advantages, and applications of hydraulic submersible pumps.
Functionality of Hydraulic Submersible Pumps
At the core of a hydraulic submersible pump is its ability to function submerged in water, utilizing hydraulic power to perform its task. Unlike standard pumps that require priming and are typically positioned above the fluid source, submersible pumps are fully submerged, preventing air lock issues and ensuring efficient fluid transfer.
The design of these pumps includes a motor that drives an impeller, thereby generating the necessary hydraulic pressure. The hydraulic fluid used—often oil—is pressurized to move the impeller, creating a vacuum that draws fluid into the pump and generates flow. This system enables hydraulic submersible pumps to handle high volumes of fluids and operate under significant pressure, making them ideal for challenging environments.
Key Advantages
One of the primary advantages of hydraulic submersible pumps is their ability to operate in deep water applications where traditional pumps may falter. Their robust design allows them to withstand high pressures, making them suitable for deep well applications in both urban and rural settings. Furthermore, because they are submerged, these pumps are typically quieter than surface pumps, reducing noise pollution in residential areas.
Another significant benefit is their efficiency. Hydraulic pumps are known for their lower power consumption, resulting in reduced operational costs. Their enclosed design minimizes the risk of pump cavitation, which can damage other types of pumps and lead to costly repairs. Additionally, the submersible design reduces the need for external piping, resulting in lower installation costs and simpler maintenance.
Applications of Hydraulic Submersible Pumps
hydraulic submersible pump
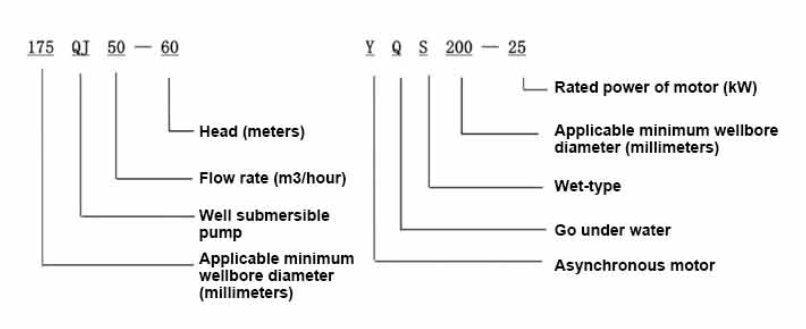
Hydraulic submersible pumps find applications across various sectors owing to their versatility and reliability. Here are a few notable examples
1. Construction In construction sites, hydraulic submersible pumps are utilized for dewatering excavations, managing groundwater, and providing efficient drainage solutions. Their robust capacity to handle gravel-laden or sandy water helps keep sites operational during rainy seasons.
2. Mining The mining industry often relies on these pumps to manage water influx in mines, enabling safe operations and preventing flooding. They can effectively transport slurries, which contain water and solids, ensuring smooth mining processes.
3. Wastewater Management Hydraulic submersible pumps are widely used in sewage and wastewater treatment plants. They efficiently transport raw sewage and treated effluents, making them vital for maintaining sanitation and public health.
4. Irrigation Farmers and agricultural professionals utilize hydraulic submersible pumps to facilitate irrigation systems. Their ability to lift water from deep wells or bodies of water helps ensure efficient water distribution across fields, boosting crop yields.
5. Flood Control During flood emergencies, hydraulic submersible pumps are deployed to manage excess water levels effectively. Their rapid deployment and high-volume capacity make them critical in mitigating flood impacts.
Conclusion
Hydraulic submersible pumps provide unparalleled efficiency and reliability across various applications. Their ability to operate submerged in fluid, combined with their robust design to withstand high pressures, makes them indispensable in industries ranging from construction to wastewater management. As technology continues to advance, the versatility and effectiveness of hydraulic submersible pumps will likely evolve, further enhancing their role in addressing complex fluid management challenges. Understanding these pumps' functionality, advantages, and applications is paramount for industries that depend on effective water management solutions.
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
