ធ្នូ . 22, 2024 01:10 Back to list
submersible chemical pump
Understanding Submersible Chemical Pumps An Essential Tool for Various Industries
Submersible chemical pumps have become critical components in various industrial applications due to their unique design and efficiency in handling corrosive and hazardous fluids. These pumps are specifically engineered to operate submerged in the liquid they are pumping, making them highly effective for a wide range of chemicals, including acids, bases, and other corrosive substances. This article explores the intricacies, advantages, and applications of submersible chemical pumps in contemporary industries.
Design and Functionality
Submersible chemical pumps are designed to be completely immersed in the fluid they transport. This design allows for the efficient movement of chemicals from one location to another while minimizing the risk of leakage and spillage. The pump consists of a motor, impeller, and casing that are all engineered to withstand hostile chemical environments. Typically made from high-grade stainless steel or specialized plastics, these materials ensure durability and resistance to corrosion.
The primary mechanism for these pumps revolves around a motor that drives the impeller, creating a pressure differential that facilitates fluid movement through the discharge outlet. Some models incorporate a multi-stage design, allowing for higher pressure outputs, which is beneficial when pumping over long distances or against gravity.
Advantages of Submersible Chemical Pumps
1. Efficiency One of the standout features of submersible chemical pumps is their energy efficiency. Being submerged in the liquid helps keep the pump cool, which reduces the risk of overheating and extends the lifespan of the motor.
2. Space-Saving Since they operate underwater, these pumps require less surface space compared to traditional pumps, making them ideal for installations where space is at a premium.
3. Reduced Risk of Spillage As they are submerged, the risk of accidental spillage is significantly diminished. This is particularly advantageous in installations dealing with hazardous materials, as it enhances workplace safety and minimizes environmental impact.
4. Versatile Applications Submersible chemical pumps can handle a variety of fluids, making them suitable for use in numerous industries, including chemical manufacturing, wastewater treatment, mining, and agriculture.
submersible chemical pump
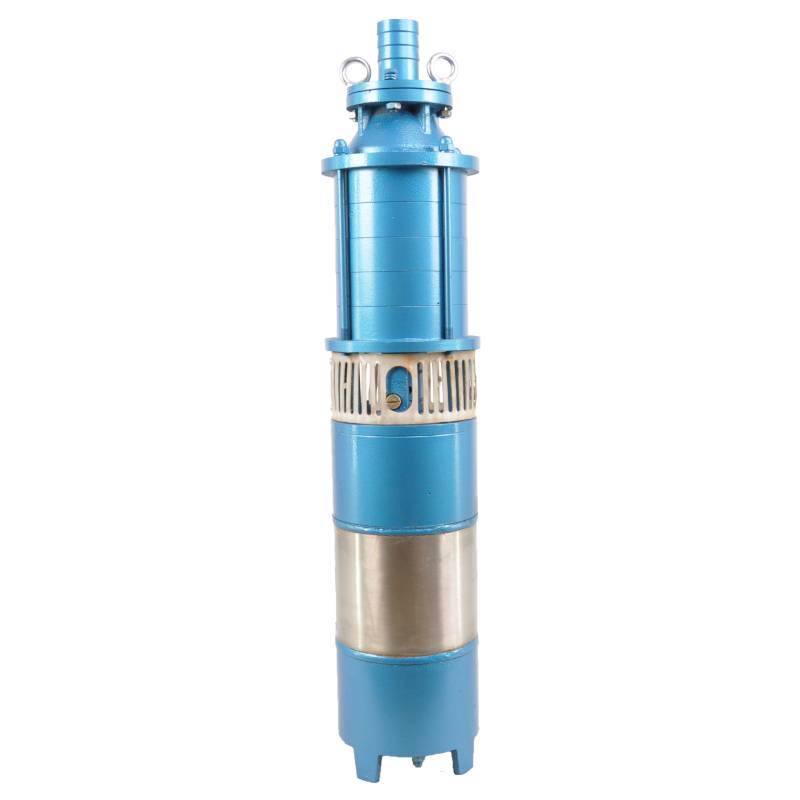
Applications
The applications of submersible chemical pumps are vast and varied. In the chemical manufacturing industry, they are used for transferring acids, alkalis, and other chemicals during production processes. In wastewater treatment, they play a crucial role in moving contaminated water through treatment facilities, ensuring that pollutants are processed efficiently.
Furthermore, in the mining sector, submersible pumps are employed to remove groundwater from mining sites, which is essential for maintaining safe working conditions. The agricultural industry also benefits from these pumps, using them for irrigation and in the transfer of fertilizers and pesticides.
Key Considerations
While submersible chemical pumps offer many advantages, there are key considerations when selecting a pump for a specific application. It is essential to evaluate the chemical compatibility of the pump materials with the fluids being handled. Using inappropriate materials can lead to pump failure and costly downtimes.
Additionally, factors such as the depth of submersion, the required flow rate, and the viscosity of the fluid should be carefully assessed. Finally, regular maintenance and inspections are crucial to ensure optimal performance and to prolong the operational life of the pump.
Conclusion
In conclusion, submersible chemical pumps are invaluable in effectively and safely transferring hazardous chemicals in various industries. Their efficient design, reduced risk of spillage, and versatility make them an ideal choice for many applications. As industries continue to prioritize safety and efficiency, the role of submersible chemical pumps will undoubtedly grow, making them a key player in modern industrial operations. As technology evolves, further advancements in materials and designs are expected, enhancing their reliability and efficiency even more.
-
submersible-sump-pump-auto-drainage-for-crawlspaces
NewsAug.22,2025
-
solar-powered-stainless-steel-submersible-well-pump-setup
NewsAug.22,2025
-
stainless-steel-well-pump-flow-rate-optimization
NewsAug.22,2025
-
water-filled-submersible-pump-fish-farm-oxygenation
NewsAug.22,2025
-
submersible-pump-in-aquaculture-and-fish-farming
NewsAug.22,2025
-
deep-well-submersible-pump-for-drought-areas
NewsAug.22,2025
-
 submersible-sump-pump-auto-drainage-for-crawlspacesCrawlspaces, those narrow areas beneath homes, are prone to water accumulation due to leaks, groundwDetail
submersible-sump-pump-auto-drainage-for-crawlspacesCrawlspaces, those narrow areas beneath homes, are prone to water accumulation due to leaks, groundwDetail -
 solar-powered-stainless-steel-submersible-well-pump-setupHarnessing solar energy to power stainless steel submersible well pumps is a sustainable and coDetail
solar-powered-stainless-steel-submersible-well-pump-setupHarnessing solar energy to power stainless steel submersible well pumps is a sustainable and coDetail -
 stainless-steel-well-pump-flow-rate-optimizationIn various applications like agriculture, domestic water supply, and industrial use, the flow rate oDetail
stainless-steel-well-pump-flow-rate-optimizationIn various applications like agriculture, domestic water supply, and industrial use, the flow rate oDetail
