ພ.ຈ. . 22, 2024 21:06 Back to list
how do submersible well pumps work
How Do Submersible Well Pumps Work?
Submersible well pumps play a crucial role in extracting water from underground aquifers, making them essential for various applications, including residential water supply, agricultural irrigation, and industrial processes. Understanding the mechanics of how these pumps operate can shed light on their efficiency and effectiveness in providing clean water.
Structure of Submersible Well Pumps
A submersible well pump is designed to function underwater, typically in deep wells. It consists of several key components, including the motor, pump, discharge head, and protective casing. The pump and motor are housed together in a single unit, which makes installation and operation more efficient. While different models may vary, the overall structure typically features
1. Electric Motor This is located near the bottom of the pump and is sealed in a watertight casing to prevent water from entering and damaging the motor. The motor is powered by electricity and is what drives the pump's mechanism.
2. Pump Assembly Attached to the motor, the pump assembly moves the water upward through the well. The most common type of impeller used in submersible pumps is the centrifugal impeller, which converts rotational energy from the motor into kinetic energy, pushing water through the system.
3. Discharge Head This is the top part of the pump that brings the water to the surface. It often includes a check valve to prevent backflow and may have outlets for connection to water pipes.
4. Protector Casing This casing shields the pump components from well debris and protects the internal workings from environmental factors.
How Submersible Well Pumps Function
The operation of a submersible well pump begins when water is drawn into the pump through an inlet. The motor, powered by an electrical source, starts rotating the impeller at high speeds. As the impeller spins, it creates a zone of low pressure at the inlet, allowing water to be sucked in.
Once inside the pump, the water encounters the impeller blades, which are designed to push the water outward. This movement converts the kinetic energy generated by the motor into pressure energy, propelling the water upwards through a series of diverging passages called volutes. Here, the water gains velocity as pressure builds.
how do submersible well pumps work
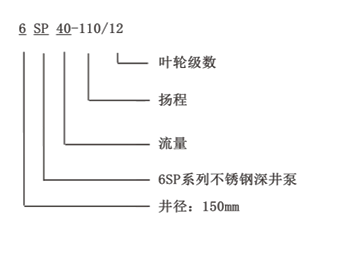
After the water rises through the pump assembly, it travels up the discharge pipe and exits through the discharge head at the surface. The pressure created by the work of the impeller ensures a steady flow of water, allowing for efficient delivery to homes, farms, or industries above ground.
Advantages of Submersible Pumps
One major advantage of submersible well pumps is their ability to operate underwater without the risk of cavitation—a condition where vapor bubbles form in a liquid and can cause damage to equipment. Because the motor is submerged, it is also effectively cooled by the surrounding water, leading to longer operational life and better performance.
Submersible pumps are also relatively quiet compared to above-ground pumps since the noise is muffled by the water. They require less maintenance, given that the motor is protected from environmental conditions and debris.
Applications and Maintenance
The versatility of submersible well pumps means they are used in various applications, including
- Domestic water supply for households - Irrigation systems for agriculture - Water supply for industrial processes - Dewatering flooded areas
Despite their durability, regular maintenance is important to ensure optimal performance. This includes checking electrical connections, inspecting seals for leaks, and ensuring that the pump is free from corroding materials and sedimentation buildup.
Conclusion
In conclusion, submersible well pumps are highly efficient devices that enable the extraction of groundwater for numerous applications. With their unique design and operational mechanisms, they have become indispensable tools in meeting our water needs. Understanding how they work not only highlights their importance but also underscores the necessity of proper maintenance for ensuring long-term reliability and performance.
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
