Sep . 19, 2024 18:38 Back to list
deep well submersible pump diagram
Understanding Deep Well Submersible Pumps A Diagrammatic Overview
Deep well submersible pumps play a crucial role in various applications, from agricultural irrigation to municipal water supply systems. These pumps are designed to operate underwater, making them essential for drawing water from deep wells where traditional pumps would be ineffective. A closer examination of the deep well submersible pump diagram reveals the intricate components that work in harmony to deliver reliable water extraction.
At the core of a deep well submersible pump is the motor, which is typically located at the lower part of the pump assembly. This submersible motor is encased in a sealed housing to protect it from water and debris. The motor drives the impellers, which are situated above it, functioning to create a pressure differential that pulls water up from the well. Impellers are critical components; they determine the pump's flow rate and efficiency. The number of stages in the pump—represented in the diagram—indicates the number of impellers in series, enabling deeper water extraction when compared to single-stage pumps.
The pump housing, often depicted in cross-section in the diagram, showcases the flow path of the water. As the motor turns the impellers, water enters through the lower intake and is propelled upward through a series of diffusers that channel the flow. This process significantly increases the pressure of the water as it moves through successive stages, allowing it to reach the surface even from considerable depths.
deep well submersible pump diagram
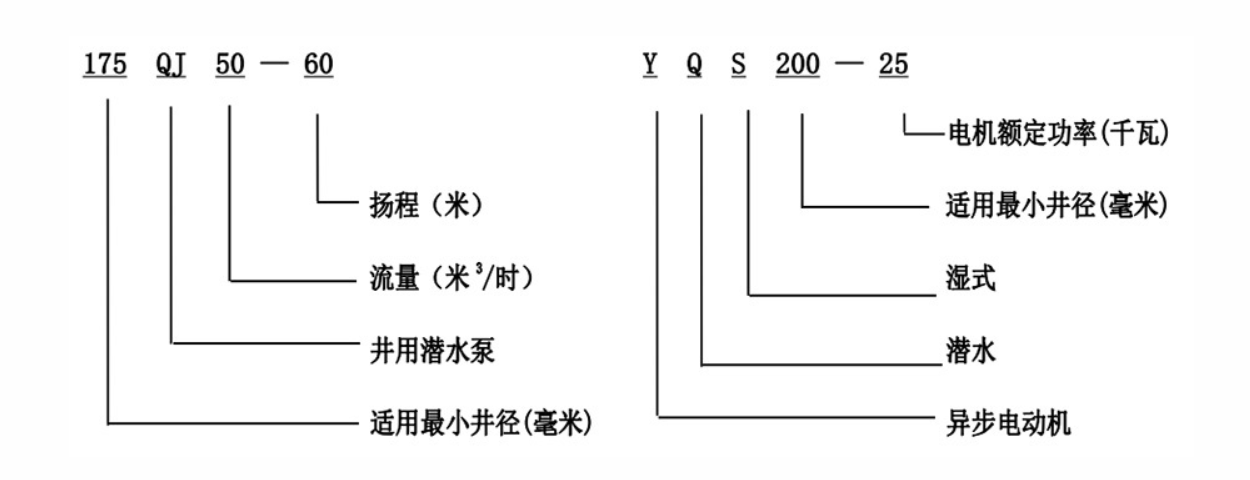
Another essential element in the diagram is the discharge head, located at the top of the pump assembly. This component connects the pump to the piping system that delivers water to the surface. The design usually includes features to facilitate easy maintenance and access to the pump without necessitating the extraction of the entire unit.
The power supply for a deep well submersible pump is typically a three-phase electrical system, which ensures efficient operation even at significant depths. The diagram often includes electrical connections that feed power to the motor. It’s noteworthy that submersible pumps are designed to withstand high voltages and currents, making them highly effective for deep well applications.
Moreover, various safety features and accessories are often illustrated, such as thermal protection to prevent overheating and check valves that prevent backflow. These additions are essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of the pump, especially in harsh operating conditions.
In summary, the deep well submersible pump diagram is a comprehensive representation of how these pumps function and the intricate components involved. Understanding these elements helps in appreciating the technology behind water extraction and its implications for resource management in various industries. As the demand for sustainable water solutions continues to rise, the role of deep well submersible pumps remains vital in meeting these needs efficiently and effectively.
-
Efficient 250QJP Peep Well Submersible Pump for Deep Well Water
NewsAug.30,2025
-
Deep Well Pump Installation Guide: Reliable Submersible Pumps
NewsAug.29,2025
-
125QJR Deep Well Submersible Pump - High Performance & Reliable Water Supply
NewsAug.28,2025
-
Water Filled Submersible Pump
NewsAug.26,2025
-
The Ultimate Solution for Clean
NewsAug.26,2025
-
SS Submersible Pump
NewsAug.26,2025
-
 Efficient 250QJP Peep Well Submersible Pump for Deep Well WaterDiscover the powerful 250QJP Peep Well Submersible Pump. Engineered for high-efficiency and reliability, it's ideal for deep well water supply, industrial, and agricultural irrigation. Get consistent performance. Explore our range today!Detail
Efficient 250QJP Peep Well Submersible Pump for Deep Well WaterDiscover the powerful 250QJP Peep Well Submersible Pump. Engineered for high-efficiency and reliability, it's ideal for deep well water supply, industrial, and agricultural irrigation. Get consistent performance. Explore our range today!Detail -
 Deep Well Pump Installation Guide: Reliable Submersible PumpsGet expert deep well pump installation for reliable, consistent water. Our durable submersible well water pumps are ideal for homes & farms. View our installation diagram & solutions.Detail
Deep Well Pump Installation Guide: Reliable Submersible PumpsGet expert deep well pump installation for reliable, consistent water. Our durable submersible well water pumps are ideal for homes & farms. View our installation diagram & solutions.Detail -
 125QJR Deep Well Submersible Pump - High Performance & Reliable Water SupplyGet reliable, high-performance water with the 125QJR Deep Well Submersible Pump. Ideal for irrigation, agriculture, and industrial deep well applications. Experience efficient, continuous water supply. Shop now!Detail
125QJR Deep Well Submersible Pump - High Performance & Reliable Water SupplyGet reliable, high-performance water with the 125QJR Deep Well Submersible Pump. Ideal for irrigation, agriculture, and industrial deep well applications. Experience efficient, continuous water supply. Shop now!Detail
