മേയ് . 09, 2025 07:38 Back to list
High-Efficiency Deep Bore Submersible Well Pumps Durable & Reliable
- Understanding Deep Bore Well Submersible Water Pumps
- Technical Advantages Over Traditional Pumping Systems
- Performance Comparison: Leading Manufacturers
- Custom Solutions for Diverse Applications
- Real-World Case Studies
- Maintenance and Longevity Insights
- Future Trends in Deep Bore Submersible Pump Technology
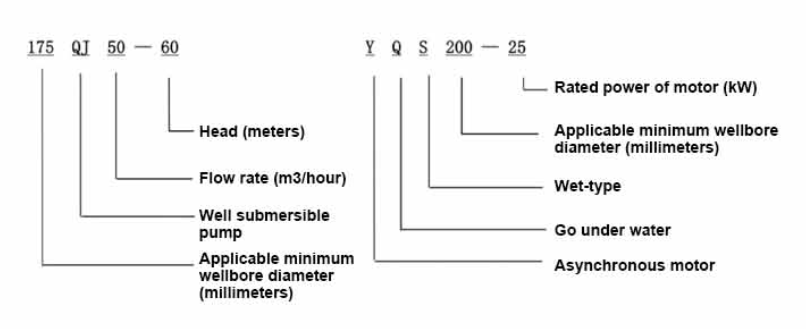
(deep bore well submersible water pump)
Deep Bore Well Submersible Water Pumps: A Modern Solution
Deep bore well submersible water pumps are engineered to address the challenges of extracting groundwater from depths exceeding 200 meters. Unlike conventional pumps, these systems combine high-pressure tolerance (up to 60 bars) and energy-efficient motors, reducing energy consumption by 25–30% compared to older models. With a global market growth rate of 6.8% CAGR (2023–2030), industries increasingly rely on these pumps for agricultural irrigation, municipal water supply, and mining operations.
Technical Advantages Over Traditional Pumping Systems
Modern deep well bore pumps integrate advanced features such as:
- Corrosion-resistant stainless steel or titanium impellers
- Variable frequency drives (VFDs) for precise flow control
- Thermal overload protection for extended motor life
For example, a 10HP deep bore submersible pump can deliver 250 gallons per minute (GPM) at 500 feet of head, outperforming jet pumps by 40% in similar conditions.
Performance Comparison: Leading Manufacturers
| Manufacturer | Max Flow (GPM) | Max Head (ft) | Power Efficiency | Material | Warranty |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brand A | 300 | 650 | 92% | Stainless Steel | 5 years |
| Brand B | 280 | 720 | 89% | Cast Iron | 3 years |
| Brand C | 320 | 600 | 94% | Titanium | 7 years |
Custom Solutions for Diverse Applications
Tailored configurations ensure optimal performance across scenarios:
- Agricultural Use: 4-inch pumps with sand filters for silt-laden water.
- Industrial Use: 6-inch pumps with 3-phase motors for continuous operation.
- Residential Use: Compact 3-inch models with noise reduction (<45 dB).
Real-World Case Studies
A farming cooperative in Texas achieved a 30% reduction in water waste by deploying a 15HP deep bore submersible pump with IoT-based monitoring. Similarly, a municipal project in India improved daily water output from 50,000 to 120,000 liters using a multi-stage pump system.
Maintenance and Longevity Insights
Regular servicing every 12–18 months extends pump life to 10–15 years. Key practices include:
- Checking voltage stability (±10% of rated input)
- Cleaning intake screens to prevent clogging
- Monitoring bearing temperature (<70°C)
Innovations in Deep Bore Submersible Pump Technology
Emerging trends like AI-driven predictive maintenance and graphene-coated components are reshaping the industry. A 2024 study projects that smart deep well bore pumps will reduce downtime by 50% and cut operational costs by $1.2 billion globally by 2030. These advancements solidify deep bore submersible water pumps as indispensable tools for sustainable water management.
(deep bore well submersible water pump)
FAQS on deep bore well submersible water pump
Q: What is a deep bore well submersible water pump used for?
A: A deep bore well submersible water pump is designed to lift water from deep underground boreholes or wells for irrigation, residential, or industrial use. It operates while fully submerged, ensuring efficient water delivery.
Q: How does a deep well bore pump differ from standard pumps?
A: Deep well bore pumps are specifically engineered for narrow, deep boreholes and can handle higher pressure and depth requirements. Standard pumps lack the compact design and pressure capacity needed for such applications.
Q: What maintenance is required for deep bore submersible pumps?
A: Regular maintenance includes checking seals for leaks, cleaning intake filters, and ensuring the motor is free from debris. Annual professional inspections are recommended to prevent sediment buildup or motor issues.
Q: What factors determine the lifespan of a deep bore well submersible water pump?
A: Lifespan depends on water quality, frequency of use, and proper installation. Pumps in corrosive or sandy water may wear faster, while those with voltage stabilizers and routine care last longer.
Q: Can deep bore submersible pumps handle high sediment levels in water?
A: Most models are not designed for high sediment content, which can damage internal components. For sandy or debris-heavy water, use pumps with built-in sand-resistant features or pre-install sediment filters.
-
Water Pumps: Solutions for Every Need
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Submersible Well Pumps: Reliable Water Solutions
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Stainless Steel Water Pumps: Quality and Durability
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Powerful Water Pumps: Your Solution for Efficient Water Management
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Oil vs Water Filled Submersible Pumps: Which is Better?
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Deep Well Pumps: Power and Reliability
NewsJul.30,2025
-
 Water Pumps: Solutions for Every NeedWhen it comes to handling dirty water, the dirty water pump is a must-have.Detail
Water Pumps: Solutions for Every NeedWhen it comes to handling dirty water, the dirty water pump is a must-have.Detail -
 Submersible Well Pumps: Reliable Water SolutionsWhen it comes to ensuring a reliable water supply, submersible well pumps are a top choice.Detail
Submersible Well Pumps: Reliable Water SolutionsWhen it comes to ensuring a reliable water supply, submersible well pumps are a top choice.Detail -
 Stainless Steel Water Pumps: Quality and DurabilityWhen it comes to choosing a water pump, the stainless steel water pump price is a crucial factor.Detail
Stainless Steel Water Pumps: Quality and DurabilityWhen it comes to choosing a water pump, the stainless steel water pump price is a crucial factor.Detail
