Nov . 13, 2024 05:55 Back to list
1 3 hp submersible pump
Understanding 1% 3% HP Submersible Pumps Efficiency and Applications
In the world of fluid management and water engineering, the significance of submersible pumps cannot be overstated. Among these, the 1% 3% HP submersible pumps stand out due to their unique efficiency ratings and suitability for various applications. This article will delve into what these pumps are, their working principle, and their practical uses across different industries.
What is a Submersible Pump?
A submersible pump is designed to operate while fully submerged in liquid. Unlike other pumps that pull water from a source, submersible pumps push water to the surface, utilizing an electric motor that is hermetically sealed. This feature allows them to operate underwater without the risk of short circuits or damage, making them ideal for a range of applications, from dewatering construction sites to draining flooded areas.
Understanding the 1% 3% HP Rating
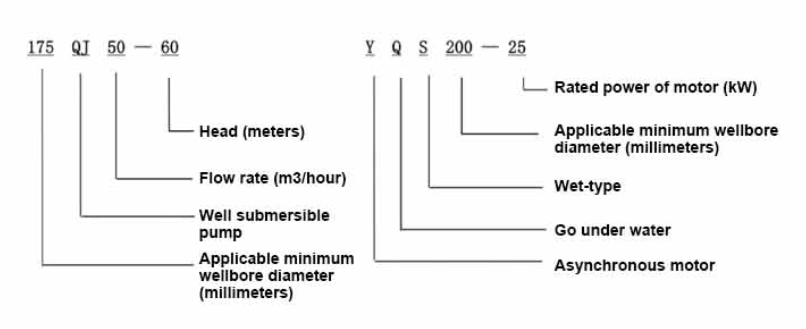
The 1% 3% HP designation refers primarily to the pump's efficiency and horsepower rating. In this context
- HP (Horsepower) This indicates the power output of the pump's motor. Typically, submersible pumps come in various horsepower ratings, with the choice depending on the required pumping capacity. A 1 HP or 3 HP pump indicates that the pump can effectively handle different flow rates and pressures.
- Efficiency Ratings (1% - 3%) This specification refers to the efficiency of the motor under different load conditions. For example, if a pump operates at 1% efficiency, it means that only a small fraction of the input energy is effectively utilized for pumping water, while a significant portion may be lost as heat. Conversely, a 3% efficiency rating suggests a better performance where more energy is converted into useful work. Understanding these ratings is crucial for selecting a pump that minimizes energy costs while maximizing output.
Applications of 1% 3% HP Submersible Pumps
1 3 hp submersible pump
Submersible pumps are versatile and used in various industries and scenarios, including
1. Agriculture Farmers utilize submersible pumps for irrigation systems, delivering water from wells to crops. Efficient water usage is essential for maximizing yield, and pumps with an ideal efficiency rating can ensure lower operational costs.
2. Construction During construction projects, dewatering is often necessary to keep sites dry and safe. Submersible pumps keep excavations free from water, preventing delays caused by flooding or excessive water accumulation.
3. Industrial Use In industries that require constant water supply, such as manufacturing and processing plants, submersible pumps facilitate the movement of chemicals and other fluids while maintaining efficiency.
4. Wastewater Management Submersible pumps are essential in sewage systems and treatment plants, where they help move wastewater from lower to higher elevations during the treatment process.
5. Residential Use In home applications, submersible pumps can help maintain basements, swimming pools, and aquariums. Homeowners appreciate their efficiency and reliability when it comes to managing groundwater and drainage needs.
Conclusion
1% 3% HP submersible pumps are integral to a variety of sectors, thanks to their effectiveness in moving water and other fluids efficiently. With a combination of specific horsepower ratings and efficiency classifications, these pumps cater to different needs, maximizing performance while reducing energy consumption. Understanding the parameters involved in selecting the right submersible pump can significantly impact operational success across farming, construction, industry, and residential applications.
In a world increasingly focused on sustainability and efficiency, investing in high-performance submersible pumps is a step towards achieving better resource management and operational effectiveness. Whether for agricultural use, construction dewatering, or industrial applications, the choice of the right pump can make all the difference.
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
