Nov . 06, 2024 14:36 Back to list
Flow Rate of 1.5% 20 HP Submersible Pumps Explained and Analyzed
Understanding the Flow Rate of a 1.5% 20 HP Submersible Pump
When it comes to efficient water management, submersible pumps play a crucial role in industries ranging from agriculture to municipal water systems. Among the myriad options available, a 1.5% 20 horsepower (HP) submersible pump has emerged as a popular choice due to its significant capabilities and efficiency. Understanding the flow rate of such a pump is essential for optimizing its performance in various applications.
What is a Submersible Pump?
A submersible pump is a device designed to operate while submerged in fluid. It consists of a motor that is hermetically sealed, allowing it to operate underwater without the risk of damage. This design is particularly effective for pumping water from wells, tanks, and other sources, making it ideal for both residential and industrial purposes.
The Significance of Horsepower
Horsepower is a measure of the pump's power output. A 20 HP submersible pump indicates substantial lifting and flow capabilities, which is crucial when dealing with significant volumes of water. The efficiency and energy consumption of the pump rely heavily on its horsepower rating. For a 1.5% 20 HP pump, slightly above standard efficiency levels can lead to more manageable operational costs and improved overall performance.
Flow Rate What You Need to Know
Flow rate, typically measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per second (L/s), is a fundamental performance metric for pumps. For a 20 HP submersible pump, the flow rate can vary based on several factors, including the design of the pump, the diameter of the discharge pipe, and the depth from which water is being drawn.
On average, a 20 HP submersible pump can achieve flow rates ranging from 60 to 100 GPM at optimal operating conditions. This output is often sufficient for agricultural irrigation, dewatering applications, and other industrial tasks. However, the actual flow rate will depend on specific requirements and operational parameters.
1.5 hp submersible pump flow rate
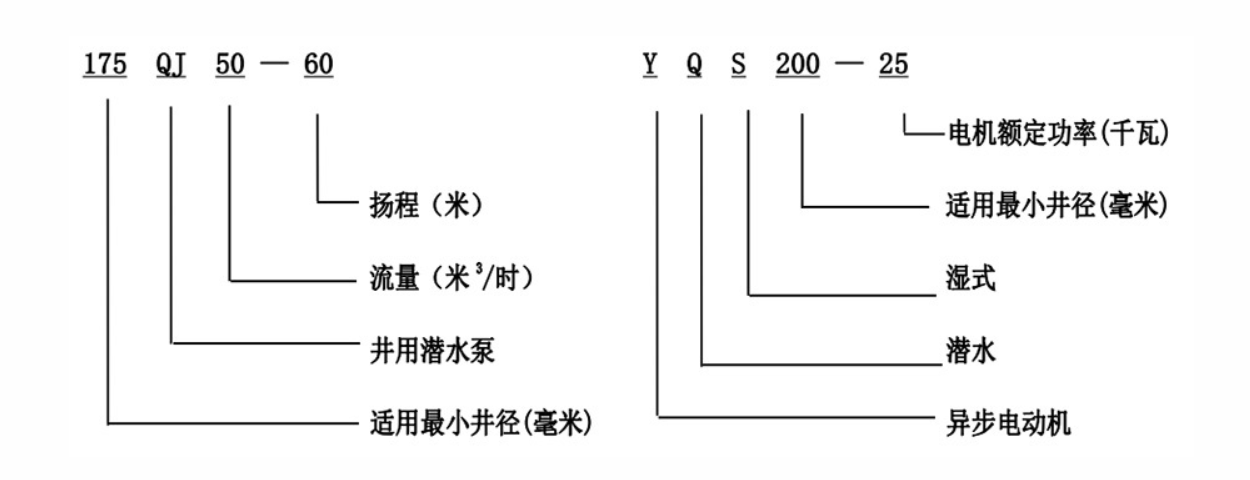
Factors Affecting Flow Rate
1. Head Pressure The vertical distance that the pump must lift the water greatly influences flow. Increased head pressure reduces flow rate, as the pump has to work harder to move water against gravity.
2. Pipe Diameter The size of the discharge pipe impacts flow rate, as narrower pipes can create friction and resistance, reducing the amount of water that can be transported effectively.
3. Pump Efficiency The design and state of the pump itself, including wear and tear, can affect performance. Regular maintenance can ensure optimal efficiency and longer lifespans.
4. Fluid Characteristics The type of fluid being pumped can affect the operation. For example, pumping thick liquids will require more energy and decrease flow rates compared to water.
Applications of a 1.5% 20 HP Submersible Pump
The versatility of a 20 HP submersible pump means it can be deployed in various applications. In agriculture, these pumps can irrigate large fields efficiently, ensuring crops receive adequate water. In construction, they are vital for dewatering sites, keeping excavations clear of excess water. Municipal systems utilize these pumps for sewage and stormwater management, providing clean water supply and preventing flooding.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the flow rate of a 1.5% 20 HP submersible pump is essential for anyone considering its application in their operations. By examining factors such as head pressure, pipe diameter, and overall pump efficiency, users can optimize their systems for maximum performance. Whether for agricultural, industrial, or municipal applications, leveraging the capabilities of a 20 HP submersible pump can lead to enhanced efficiency, reduced operational costs, and sustainable water management solutions. As technology advances, these pumps will continue to evolve, providing even greater reliability and effectiveness in water handling tasks.
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
