Oct . 11, 2024 07:33 Back to list
3 in submersible well pump
Understanding 3% in Submersible Well Pumps
Submersible well pumps are essential pieces of equipment used in various applications, from residential water supply to agricultural irrigation and even industrial processes. These pumps are designed to operate underwater, often submerged in a well, to draw water from deep underground sources. At the heart of discussing submersible well pumps is the significance of their efficiency, which can be represented by a factor of 3%. This article seeks to explore the importance of the 3% efficiency metric, the working principles of submersible well pumps, and their application across different sectors.
What is a Submersible Well Pump?
A submersible well pump is a type of pump that is hermetically sealed to prevent flooding and is submerged in the fluid it is pumping. These pumps are typically used in wells that tap into aquifers to extract groundwater. The design allows them to operate efficiently in deep wells without requiring a long vertical column, which can create pressure losses.
The Significance of 3% Efficiency
When we refer to “3% in submersible well pumps,” we must consider what this percentage represents. Although submersible pumps can have efficiency ratings significantly higher than 3%, maintaining a good efficiency level is crucial. An efficiency rating of 3% may pertain to certain loss factors in some contexts, such as mechanical losses or inefficiencies arising from the pump’s operating conditions. However, in practical applications, users typically look for pumps that maintain at least 70-90% efficiency under optimal conditions.
Achieving high efficiency in pump systems translates to reduced energy consumption. For commercial and industrial applications, where pumps operate continuously or at high volumes, even a small percentage in efficiency can lead to significant cost savings over time and lower carbon emissions.
Working Principles of Submersible Well Pumps
Submersible pumps operate using a multi-stage design, with a series of impellers that lift water from underground sources
. The basic components of a submersible well pump include3 in submersible well pump
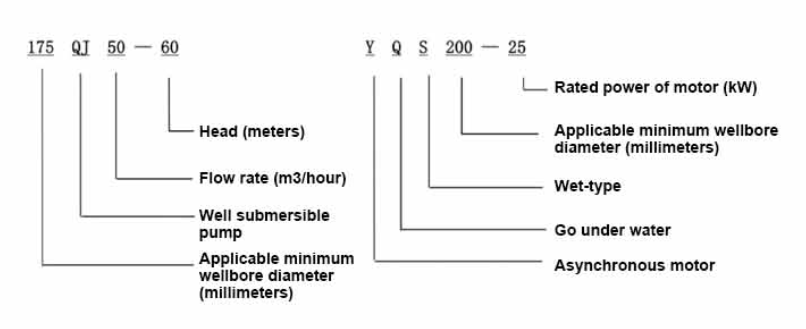
1. Motor The motor is located at the bottom of the well and directly powers the impellers. It is designed to work underwater and has protective waterproof seals.
2. Impellers These are the rotating elements that create the pressure needed to push water to the surface. More impellers generally mean higher pressure and efficiency.
3. Diffusers Located between the impellers, these components help convert the kinetic energy generated by the impellers into pressure energy.
4. Suction Strainer This prevents large debris from entering the pump and causing potential damage.
5. Discharge Head This is the section above ground where water exits the pump, allowing for connection to the water supply system.
Applications of Submersible Well Pumps
Submersible well pumps are widely used across many sectors. In residential settings, they provide a reliable water supply for households, particularly in rural areas where municipal water may not be available. They are critical for agricultural irrigation, ensuring crops receive the necessary water supply. In industrial applications, these pumps facilitate water management, aiding in processes like cooling systems and manufacturing operations.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the significance of efficiency metrics—such as the mentioned 3%—is essential for selecting and operating submersible well pumps effectively. These pumps play a crucial role in modern water supply systems, demonstrating their value in various applications. By choosing efficient models, users can achieve substantial cost savings and contribute to sustainable water management practices. The evolution of pump technology continues to enhance their performance, ensuring that they meet the increasing demand for water while minimizing energy use and environmental impact.
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
