Nov . 15, 2024 03:36 Back to list
3 submersible pumps
Understanding 3% Submersible Pumps A Comprehensive Guide
Submersible pumps are an essential tool in various industries, including agriculture, construction, and wastewater management. These pumps are designed to operate submerged in water, making them highly efficient for moving liquids from one place to another. In this article, we will focus on the concept of 3% submersible pumps, exploring their functionality, applications, and benefits.
What Are Submersible Pumps?
Submersible pumps are devices that are placed underwater to pump liquids to the surface. Unlike above-ground pumps, which draw water through a suction line, submersible pumps push the fluid to the surface. This design allows them to operate more efficiently, especially in deep-well applications where traditional pumps would struggle.
The term “3% submersible pump” typically refers to the efficiency rating of the pump. Efficiency is a crucial factor in determining the pump's performance, as it directly impacts energy consumption and operational costs. A 3% efficiency rating may not be commonly referenced in professional settings, but it signifies the importance of selecting pumps with optimal performance for specific applications.
How Do Submersible Pumps Work?
Submersible pumps consist of a motor, a pump, and a protective casing. The motor drives the impeller, which moves the liquid through the pump. When the pump is submerged, the surrounding water provides pressure, allowing the device to operate effectively at varied depths.
There are two main types of submersible pumps sewage pumps and well pumps. Sewage pumps are used to transport waste and sewage, while well pumps are designed for drawing water from underground sources. Regardless of the type, the principle remains the same—creating pressure to push the liquid to the desired location.
Applications of Submersible Pumps
Submersible pumps are utilized in numerous applications, including
3 submersible pumps
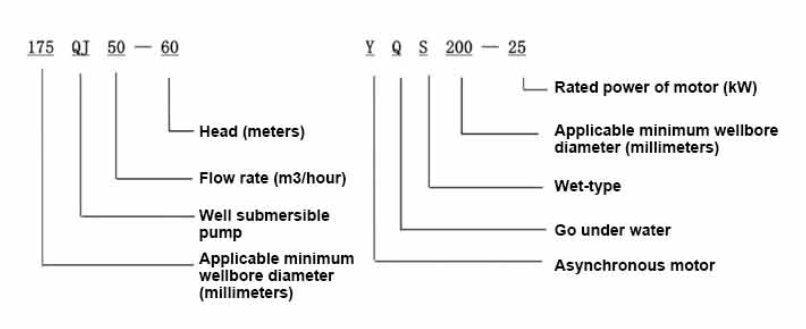
1. Water Supply These pumps are commonly used in residential and commercial settings to draw water from wells and reservoirs. 2. Irrigation Farmers use submersible pumps to irrigate crops, ensuring a steady water supply for agricultural practices. 3. Sewage and Wastewater Management In municipal applications, these pumps are critical for transporting sewage and stormwater to treatment facilities. 4. Construction They are often used to dewater construction sites, keeping the area dry and safe for workers.
Advantages of Using Submersible Pumps
1. Efficiency Submersible pumps are typically more energy-efficient than their non-submersible counterparts, as they do not need to lift water against gravity.
2. Reliable Performance These pumps can operate in deep locations without losing performance, making them suitable for various applications where traditional pumps fail.
3. Reduced Noise Being submerged, these pumps operate quietly, making them ideal for residential areas and noise-sensitive environments.
4. Versatility Available in various sizes and designs, submersible pumps can be tailored for specific applications, ensuring optimal performance.
5. Durability Made from corrosion-resistant materials, these pumps are designed to withstand harsh operating conditions.
Conclusion
In summary, submersible pumps, including those with a 3% efficiency rating, play a pivotal role in various sectors. Their ability to efficiently move liquids from subterranean sources to the surface makes them indispensable in modern applications. Whether for irrigation, sewage management, or water supply, understanding their functionality, applications, and benefits can help individuals and businesses select the right pump for their needs. With their numerous advantages, it's evident why submersible pumps are a trusted solution for liquid transfer challenges worldwide.
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
