Nov . 10, 2024 10:47 Back to list
Exploring the Benefits of 4% Submersible Pumps for Efficient Water Management Systems
Understanding 4% Submersible Pumps A Comprehensive Guide
Submersible pumps are critical equipment used in a variety of applications, including groundwater extraction, sewage displacement, and oil well production. Among the different types of submersible pumps available in the market, the 4% submersible pump stands out for its efficient design and capabilities. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of what a 4% submersible pump is, its applications, benefits, and considerations for selecting the right pump for your needs.
What is a 4% Submersible Pump?
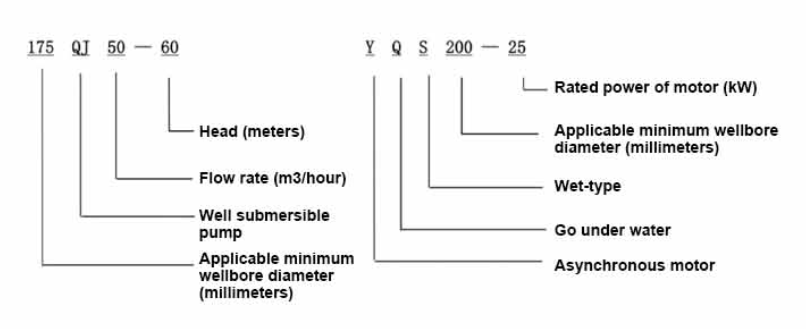
A 4% submersible pump refers to a specific type of pump that is primarily used for liquid handling applications where the pump is submerged in the fluid it needs to pump. The 4% typically refers to the pump's performance capabilities, often indicating its efficiency in lifting fluids over a certain height or its flow rate under given conditions. These pumps are equipped with a hermetically sealed motor that is submerged along with the pump, allowing them to operate efficiently at significant depths, thereby eliminating the need for priming.
Applications of 4% Submersible Pumps
The versatility of 4% submersible pumps makes them suitable for a range of applications
1. Groundwater Extraction They are widely used for borehole and well pumping, where the pump needs to lift water from underground aquifers. 2. Sewage and Wastewater Management Many municipalities rely on submersible pumps to manage sewage and wastewater efficiently, ensuring that waste is moved to treatment facilities.
3. Irrigation Farmers utilize these pumps for irrigation systems, particularly in fields where water needs to be drawn from wells or reservoirs.
4. Agricultural Applications Irrigation and water management systems in agriculture often use 4% submersible pumps due to their reliability and capacity to handle varied fluid types.
5. Industrial Use Industries use these pumps for various processes that require fluid transfer, including chemicals, oils, and other liquids.
6. Firefighting Some fire departments use portable submersible pumps to deliver water in rural areas where traditional fire hydrants are not available.
Advantages of 4% Submersible Pumps
There are several advantages to using 4% submersible pumps
1. Efficiency These pumps are designed to operate underwater, which allows them to maintain higher efficiency levels, particularly when moving fluids from low-lying locations.
4 submersible pump
2. Space-Saving Design The compact design of submersible pumps allows them to fit into narrow spaces or those with limited access, making them ideal for various installations.
3. Reduced Noise Pollution Operating underwater minimizes noise pollution, which is particularly beneficial in residential areas or noise-sensitive environments.
4. Lower Operating Costs Due to their efficiency, submersible pumps often result in lower energy costs when compared to traditional above-ground pumps.
5. Durability and Longevity Made from corrosion-resistant materials, submersible pumps are designed to withstand harsh conditions, prolonging their service life.
Selecting the Right 4% Submersible Pump
When choosing a 4% submersible pump, several factors must be considered
1. Fluid Characteristics Analyze the type of fluid being pumped, including viscosity, temperature, and corrosiveness.
2. Flow Rate Requirements Understanding the required flow rate is essential for selecting a pump that can meet operational demands.
3. Head Requirements Assess the vertical distance the pump needs to move the fluid, as this will influence the pump's design and motor power.
4. Power Supply Ensure the pump’s power requirements align with available electrical supply options.
5. Material and Construction Select a pump made from materials suited to the fluid being pumped to prevent corrosion and ensure longevity.
Conclusion
4% submersible pumps are invaluable tools across various industries and applications. Their design, efficiency, and versatility make them a top choice for handling fluid transfer tasks, whether it’s extracting groundwater, managing wastewater, or supplying irrigation. Understanding their capabilities and selecting the right pump for specific needs can significantly enhance operational efficiency and reliability in fluid management. As technology advances, we can expect further improvements in the performance and functionality of submersible pumps, solidifying their role as a critical component in modern fluid handling applications.
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
