Jul . 29, 2024 21:26 Back to list
Common Issues Faced with Deep Well Submersible Pumps and Their Effective Solutions
Common Problems with Deep Well Submersible Pumps
Deep well submersible pumps are essential components in various applications, including agricultural irrigation, municipal water supply, and industrial processes. These pumps are designed to operate submerged in water, allowing them to draw water from significant depths efficiently. However, like any mechanical system, they are prone to certain problems that can affect their performance and longevity. Understanding these issues can help users maintain their pumps effectively and avoid costly downtime.
1. Overheating
Overheating is a common issue for deep well submersible pumps, often resulting from continuous operation or insufficient cooling. When a pump runs too hot, it can lead to permanent damage to the motor, seals, and impellers. Common causes of overheating include inadequate water supply, excessive friction due to a clogged intake, or improper installation. Regular maintenance, including checking for debris in the intake and ensuring the pump is appropriately sized for the application, can help mitigate this problem.
Cavitation occurs when there is a rapid change in pressure in the pump, leading to the formation of vapor bubbles. When these bubbles collapse, they create shock waves that can cause significant damage to the pump components, especially the impellers. Factors contributing to cavitation include high flow rates, low suction pressure, and excessive elevation of the pump. To prevent cavitation, it is crucial to ensure that the pump operates within its recommended parameters and to avoid sudden changes in flow rates.
3. Electrical Failures
deep well submersible pump problems
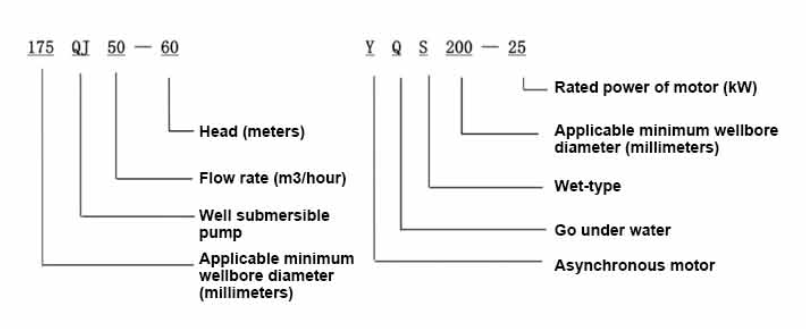
Electrical issues are another common problem faced by deep well submersible pumps. This can include motor burn-out due to over-voltage, under-voltage, or phase loss. Additionally, moisture intrusion into the electrical connections can lead to short circuits, causing the pump to fail. Implementing surge protection devices and regular inspections of electrical components can help prevent electrical failures. Moreover, ensuring that the pump is correctly wired and that the electrical supply is stable is essential for long-term operation.
4. Mechanical Seal Failure
Mechanical seals play a crucial role in preventing water from entering the motor housing. Seal failures can occur due to wear, abrasive materials in the water, or improper installation. When seals fail, water can infiltrate the motor, leading to catastrophic damage. Regular inspection of seals and replacing them as part of a preventive maintenance routine can help avoid this issue. Additionally, selecting pumps with robust sealing technologies can enhance durability in challenging environments.
5. Sediment Build-Up
In many deep well applications, sediment and debris can accumulate within the pump or the well casing itself. This build-up can lead to reduced efficiency, increased power consumption, and even pump failure. Regularly monitoring water quality and conducting routine cleaning and maintenance of the well can significantly reduce the risk of sediment-related issues. Implementing filtration systems may also help in reducing debris entering the pump.
Conclusion
Deep well submersible pumps are invaluable for various applications, but they are not immune to problems that can compromise their operation. Overheating, cavitation, electrical failures, mechanical seal failure, and sediment build-up are some of the most common issues that users may encounter. By understanding these problems and adopting preventive maintenance measures, users can ensure the efficient and reliable operation of their submersible pumps for years to come. Regular inspections and timely interventions can not only extend the life of the pump but also contribute to overall system efficiency, ultimately saving time and resources.
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
