Jun . 26, 2024 18:44 Back to list
Deep Well Pump Operation Mechanism
Deep Well Pumps An In-Depth Look at Their Working Principle
Deep well pumps are essential components in the realm of water supply and irrigation systems. These pumps are specifically designed to extract water from depths of up to several hundred feet below ground level. Their exceptional performance is primarily attributed to their sophisticated working principle, which involves a series of intricate processes that work together seamlessly to achieve the desired outcome.
At the heart of a deep well pump is an electric motor. This motor serves as the primary source of power, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy. The motor is typically housed within a protective casing and is designed to operate under high pressure and temperature conditions commonly encountered in deep well applications.
The motor is connected to a pump shaft, which in turn is attached to a multistage impeller. The impeller is a critical component of the pump, as it is responsible for drawing water into the pump and increasing its pressure. As the impeller rotates, it forces water through a series of progressively smaller channels, thereby increasing its velocity and pressure.
The pressurized water is then directed through a manifold system, which evenly distributes it throughout the distribution network
The pressurized water is then directed through a manifold system, which evenly distributes it throughout the distribution network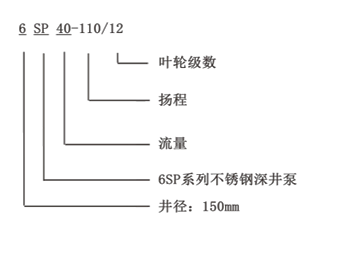 The pressurized water is then directed through a manifold system, which evenly distributes it throughout the distribution network
The pressurized water is then directed through a manifold system, which evenly distributes it throughout the distribution network
The pressurized water is then directed through a manifold system, which evenly distributes it throughout the distribution network
The pressurized water is then directed through a manifold system, which evenly distributes it throughout the distribution network deep well pump working principle. This ensures that water is delivered to all parts of the system with equal pressure, providing a consistent and reliable water supply.
One of the key advantages of deep well pumps is their ability to efficiently extract water from large volumes of aquifers. This makes them particularly suitable for applications such as irrigation, where large amounts of water are required to meet crop demands. Additionally, deep well pumps are generally more cost-effective than other types of water pumping systems, making them a popular choice for many farmers and homeowners.
In conclusion, deep well pumps are remarkable pieces of engineering, capable of extracting water from depths that would be otherwise inaccessible. Their working principle, involving a combination of electric motors, pump shafts, and multistage impellers, enables them to deliver large volumes of water with remarkable efficiency. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative designs and improvements in the performance of these vital machines.
deep well pump working principle. This ensures that water is delivered to all parts of the system with equal pressure, providing a consistent and reliable water supply.
One of the key advantages of deep well pumps is their ability to efficiently extract water from large volumes of aquifers. This makes them particularly suitable for applications such as irrigation, where large amounts of water are required to meet crop demands. Additionally, deep well pumps are generally more cost-effective than other types of water pumping systems, making them a popular choice for many farmers and homeowners.
In conclusion, deep well pumps are remarkable pieces of engineering, capable of extracting water from depths that would be otherwise inaccessible. Their working principle, involving a combination of electric motors, pump shafts, and multistage impellers, enables them to deliver large volumes of water with remarkable efficiency. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative designs and improvements in the performance of these vital machines.
 The pressurized water is then directed through a manifold system, which evenly distributes it throughout the distribution network
The pressurized water is then directed through a manifold system, which evenly distributes it throughout the distribution network
The pressurized water is then directed through a manifold system, which evenly distributes it throughout the distribution network
The pressurized water is then directed through a manifold system, which evenly distributes it throughout the distribution network deep well pump working principle. This ensures that water is delivered to all parts of the system with equal pressure, providing a consistent and reliable water supply.
One of the key advantages of deep well pumps is their ability to efficiently extract water from large volumes of aquifers. This makes them particularly suitable for applications such as irrigation, where large amounts of water are required to meet crop demands. Additionally, deep well pumps are generally more cost-effective than other types of water pumping systems, making them a popular choice for many farmers and homeowners.
In conclusion, deep well pumps are remarkable pieces of engineering, capable of extracting water from depths that would be otherwise inaccessible. Their working principle, involving a combination of electric motors, pump shafts, and multistage impellers, enables them to deliver large volumes of water with remarkable efficiency. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative designs and improvements in the performance of these vital machines.
deep well pump working principle. This ensures that water is delivered to all parts of the system with equal pressure, providing a consistent and reliable water supply.
One of the key advantages of deep well pumps is their ability to efficiently extract water from large volumes of aquifers. This makes them particularly suitable for applications such as irrigation, where large amounts of water are required to meet crop demands. Additionally, deep well pumps are generally more cost-effective than other types of water pumping systems, making them a popular choice for many farmers and homeowners.
In conclusion, deep well pumps are remarkable pieces of engineering, capable of extracting water from depths that would be otherwise inaccessible. Their working principle, involving a combination of electric motors, pump shafts, and multistage impellers, enables them to deliver large volumes of water with remarkable efficiency. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative designs and improvements in the performance of these vital machines. Latest news
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
