Oct . 02, 2024 03:13 Back to list
Submersible Deep Well Water Pumps for Efficient and Reliable Water Extraction Solutions
Deep Well Water Pump Submersible A Comprehensive Overview
Water is an essential resource, and access to clean, freshwater is pivotal for both household and agricultural needs. In many regions, especially those devoid of surface water, deep well water pumps, particularly submersible pumps, play a crucial role in drawing water from aquifers located deep beneath the ground. This article delves into the function, advantages, installation, maintenance, and considerations surrounding submersible deep well water pumps.
Understanding Submersible Deep Well Pumps
Submersible deep well pumps are electric pumps designed to be submerged underwater, usually within a borehole or well. Unlike conventional pumps that sit above ground, submersible pumps push water to the surface rather than pull it, making them more efficient for deep-well applications. These pumps consist of a motor and a pump body, both of which are sealed to prevent water from entering and causing damage. The motor drives the impeller, which moves water through the pump and up the delivery pipeline to the surface.
Advantages of Submersible Deep Well Pumps
The use of submersible pumps offers several advantages. First, their design inherently minimizes the risk of cavitation, a phenomenon where vapor bubbles form in a liquid and can cause damage to the pump. Since submersible pumps are placed underwater, they maintain prime and reduce the chances of air entering the system.
Moreover, submersible pumps can operate efficiently in deeper wells, typically reaching depths of over 100 feet. This makes them suitable for agricultural applications, residential water supply, and even large-scale industrial uses. Additionally, these pumps often have a longer lifespan compared to above-ground pumps, due to their thermal efficiencies and the cooling effects of the surrounding water.
Installation Considerations
deep well water pump submersible
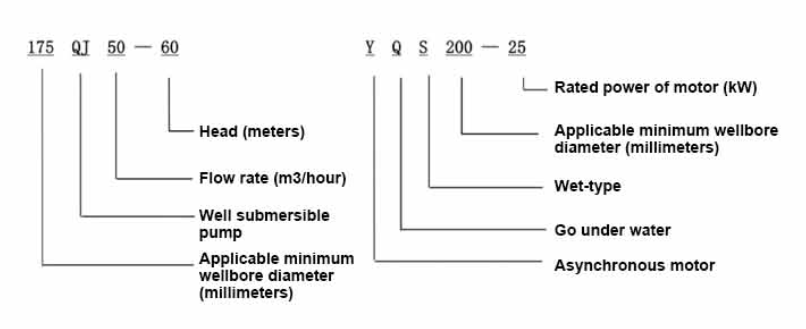
Installation of a submersible deep well pump involves several critical steps. The first is to determine the suitable pump size and capacity based on the well's depth and the intended water output. The borehole must be clean and properly lined to accommodate the pump. Installation typically requires specialized tools and expertise, owing to the depth and technical requirements involved.
Once installed, the pump should be connected to a power source, and a discharge pipe must be set up to lead water to the desired location. Proper installation ensures optimal performance and helps avoid common problems such as pump burnout or failure.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Maintaining a submersible deep well pump is essential to ensure longevity and efficient operation. Regular inspection helps identify wear and tear on components such as seals, bearings, and impellers. Operators should also check for signs of corrosion or electrical issues, particularly in the motor and control systems.
In case of malfunction, common troubleshooting steps include checking the power supply, ensuring that the pump is free of blockages, and verifying that the pressure switch is functioning correctly. Many manufacturers recommend routine professional servicing to keep the pump in top condition.
Conclusion
Submersible deep well pumps are indispensable in providing access to groundwater in areas without surface water. Their efficiency, longevity, and adaptability make them suitable for various applications, from residential use to large agricultural operations. Proper installation, along with regular maintenance, guarantees that these pumps perform effectively, ensuring a reliable water supply for years to come. As water scarcity continues to be a global challenge, the importance of technology, such as submersible deep well pumps, cannot be overstated in our quest for sustainable water management.
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
