Nov . 16, 2024 00:02 Back to list
diagram of submersible well pump
Understanding Submersible Well Pumps A Diagrammatic Approach
Submersible well pumps are essential devices utilized in various applications, particularly in agricultural, municipal, and residential settings to draw water from wells. Their efficiency and effectiveness can be appreciated by examining their design and functioning through a diagrammatic representation.
Structure and Components
A submersible well pump is typically comprised of several key components that work in unison to ensure optimal performance. The most significant parts include the pump motor, impellers, volutes, and discharge head. The motor is hermetically sealed to prevent water from entering, ensuring longevity and reliability in operation.
The impellers play a crucial role in generating the hydraulic lift necessary to transport water from below the surface to the desired height. When the motor rotates, the impellers create kinetic energy that propels water upward through the volutes, which gradually convert this kinetic energy into pressure energy. The discharge head is the final component that allows the water to flow out from the pump into the intended pipe system or storage tank.
Operational Principle
The operational principle of a submersible well pump is relatively straightforward. These pumps are submerged in the water they need to lift, allowing them to eliminate issues related to priming, which often affects other types of pumps. Since they are installed deep within the well, they can take advantage of the gravitational force and minimize the risk of cavitation, which can damage the pump mechanisms.
diagram of submersible well pump
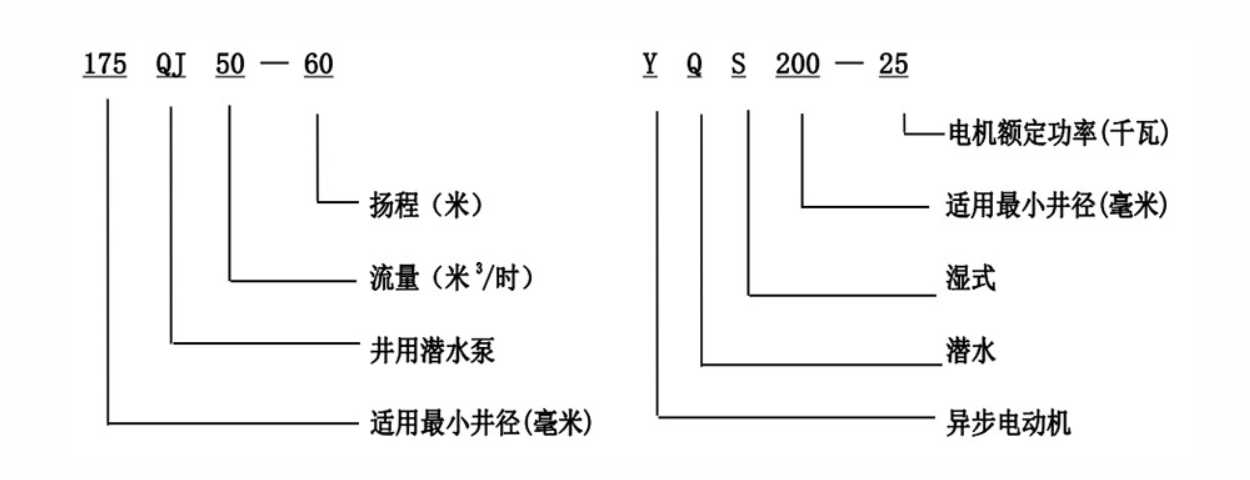
A diagram of a submersible well pump showcases how these components interact with each other. It highlights the enclosed motor that prevents water ingress and the vertical configuration that maximizes water lifting efficiency. The placement of the motor below the water level also aids in cooling, ensuring the system runs smoothly over extended periods.
Advantages of Submersible Well Pumps
The submersible design offers several advantages over traditional pumps. One key benefit is their ability to pump water from great depths. Unlike surface pumps that are limited to shallow sources, submersible well pumps can reach hundreds of feet below the surface, making them suitable for deep wells. Additionally, these pumps are more energy-efficient, as they do not waste energy on creating suction.
Their quiet operation is another plus, as they are submerged beneath the water, minimizing noise pollution. This feature makes them ideal for residential areas where noise can be a concern. Moreover, the compact design of submersible pumps allows for easier installation and maintenance, as they require less surface space.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the diagram of a submersible well pump illustrates the intricate components and their operational synergy that make these pumps indispensable for water extraction. Their efficiency, durability, and ability to operate quietly and effectively in deep wells underscore their significance in various sectors. Understanding the mechanics behind submersible well pumps can aid users in making informed choices when selecting the appropriate system for their water needs, ensuring optimal functionality and longevity.
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
