Jun . 13, 2024 11:17 Back to list
Electrically powered underwater pump
Understanding the Electric Submersible Pump A Vital Technology in Modern Industries
In the realm of oil and gas extraction, as well as various industrial applications, the electric submersible pump (ESP) stands as an essential piece of equipment, offering efficient and reliable fluid transportation. This innovative technology has revolutionized the way we handle fluids in submerged conditions, making it a cornerstone in modern industry.
An electric submersible pump, as the name suggests, is a centrifugal pump designed to be submerged directly into a liquid. It converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, propelling fluids from underground reservoirs to the surface. The unique design of ESPs allows them to operate in depths ranging from a few meters to thousands of meters, making them adaptable to a wide range of applications.
The primary components of an ESP system include a motor, a pump, a protector, and a control system. The motor, typically a squirrel-cage induction type, drives the pump, which consists of a series of impellers that create a pressure differential to lift the fluid. The protector shields the pump from solids and other debris, while the control system monitors and adjusts the pump's operation for optimal performance.
One of the key advantages of ESPs is their high efficiency. By operating close to the fluid source, they minimize pressure loss and energy consumption. Additionally, their ability to handle a wide range of fluid viscosities and solids content makes them suitable for various industries, including oil and gas, mining, wastewater management, and agriculture Additionally, their ability to handle a wide range of fluid viscosities and solids content makes them suitable for various industries, including oil and gas, mining, wastewater management, and agriculture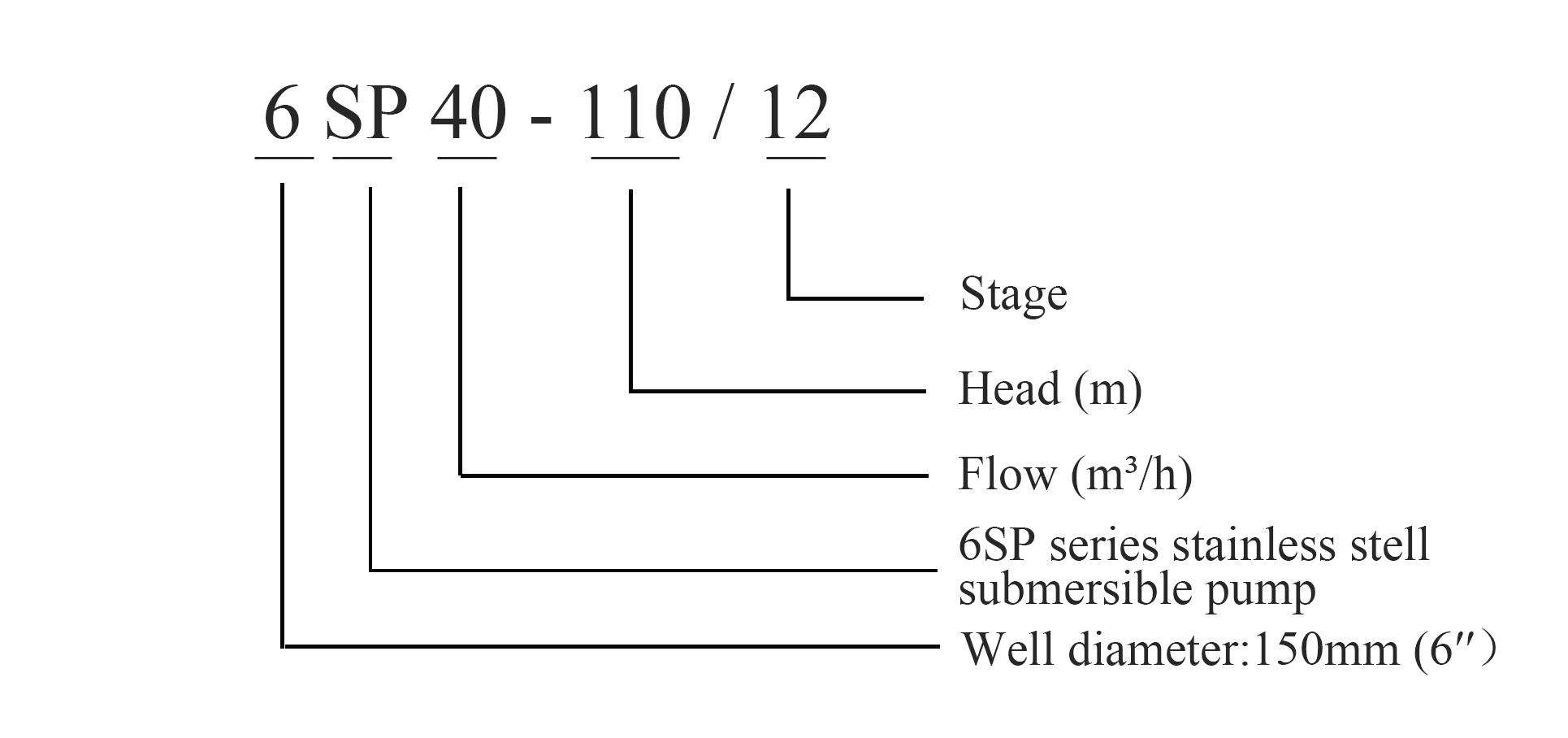 Additionally, their ability to handle a wide range of fluid viscosities and solids content makes them suitable for various industries, including oil and gas, mining, wastewater management, and agriculture Additionally, their ability to handle a wide range of fluid viscosities and solids content makes them suitable for various industries, including oil and gas, mining, wastewater management, and agriculture
Additionally, their ability to handle a wide range of fluid viscosities and solids content makes them suitable for various industries, including oil and gas, mining, wastewater management, and agriculture Additionally, their ability to handle a wide range of fluid viscosities and solids content makes them suitable for various industries, including oil and gas, mining, wastewater management, and agriculture electric submersible pump.
Maintenance is another area where ESPs excel. Since most components are submerged, they are less prone to wear and tear from external elements. However, regular monitoring and maintenance are crucial to ensure the ESP's longevity and prevent potential issues such as clogging or overheating.
Despite these benefits, ESPs also present challenges. They require a stable power supply and can be sensitive to changes in fluid properties. Moreover, installation and retrieval can be complex, often requiring specialized equipment and trained personnel.
In conclusion, the electric submersible pump is a testament to human ingenuity, providing a robust solution for fluid handling in challenging environments. As technology continues to evolve, ESPs are likely to become even more efficient and adaptable, further solidifying their position in the global industrial landscape. Whether it's extracting crude oil from deep reservoirs or managing wastewater in urban settings, the electric submersible pump remains an indispensable tool, shaping the future of fluid management.
electric submersible pump.
Maintenance is another area where ESPs excel. Since most components are submerged, they are less prone to wear and tear from external elements. However, regular monitoring and maintenance are crucial to ensure the ESP's longevity and prevent potential issues such as clogging or overheating.
Despite these benefits, ESPs also present challenges. They require a stable power supply and can be sensitive to changes in fluid properties. Moreover, installation and retrieval can be complex, often requiring specialized equipment and trained personnel.
In conclusion, the electric submersible pump is a testament to human ingenuity, providing a robust solution for fluid handling in challenging environments. As technology continues to evolve, ESPs are likely to become even more efficient and adaptable, further solidifying their position in the global industrial landscape. Whether it's extracting crude oil from deep reservoirs or managing wastewater in urban settings, the electric submersible pump remains an indispensable tool, shaping the future of fluid management.
 Additionally, their ability to handle a wide range of fluid viscosities and solids content makes them suitable for various industries, including oil and gas, mining, wastewater management, and agriculture Additionally, their ability to handle a wide range of fluid viscosities and solids content makes them suitable for various industries, including oil and gas, mining, wastewater management, and agriculture
Additionally, their ability to handle a wide range of fluid viscosities and solids content makes them suitable for various industries, including oil and gas, mining, wastewater management, and agriculture Additionally, their ability to handle a wide range of fluid viscosities and solids content makes them suitable for various industries, including oil and gas, mining, wastewater management, and agriculture electric submersible pump.
Maintenance is another area where ESPs excel. Since most components are submerged, they are less prone to wear and tear from external elements. However, regular monitoring and maintenance are crucial to ensure the ESP's longevity and prevent potential issues such as clogging or overheating.
Despite these benefits, ESPs also present challenges. They require a stable power supply and can be sensitive to changes in fluid properties. Moreover, installation and retrieval can be complex, often requiring specialized equipment and trained personnel.
In conclusion, the electric submersible pump is a testament to human ingenuity, providing a robust solution for fluid handling in challenging environments. As technology continues to evolve, ESPs are likely to become even more efficient and adaptable, further solidifying their position in the global industrial landscape. Whether it's extracting crude oil from deep reservoirs or managing wastewater in urban settings, the electric submersible pump remains an indispensable tool, shaping the future of fluid management.
electric submersible pump.
Maintenance is another area where ESPs excel. Since most components are submerged, they are less prone to wear and tear from external elements. However, regular monitoring and maintenance are crucial to ensure the ESP's longevity and prevent potential issues such as clogging or overheating.
Despite these benefits, ESPs also present challenges. They require a stable power supply and can be sensitive to changes in fluid properties. Moreover, installation and retrieval can be complex, often requiring specialized equipment and trained personnel.
In conclusion, the electric submersible pump is a testament to human ingenuity, providing a robust solution for fluid handling in challenging environments. As technology continues to evolve, ESPs are likely to become even more efficient and adaptable, further solidifying their position in the global industrial landscape. Whether it's extracting crude oil from deep reservoirs or managing wastewater in urban settings, the electric submersible pump remains an indispensable tool, shaping the future of fluid management. Latest news
-
Water Pumps: Solutions for Every Need
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Submersible Well Pumps: Reliable Water Solutions
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Stainless Steel Water Pumps: Quality and Durability
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Powerful Water Pumps: Your Solution for Efficient Water Management
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Oil vs Water Filled Submersible Pumps: Which is Better?
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Deep Well Pumps: Power and Reliability
NewsJul.30,2025
-
 Water Pumps: Solutions for Every NeedWhen it comes to handling dirty water, the dirty water pump is a must-have.Detail
Water Pumps: Solutions for Every NeedWhen it comes to handling dirty water, the dirty water pump is a must-have.Detail -
 Submersible Well Pumps: Reliable Water SolutionsWhen it comes to ensuring a reliable water supply, submersible well pumps are a top choice.Detail
Submersible Well Pumps: Reliable Water SolutionsWhen it comes to ensuring a reliable water supply, submersible well pumps are a top choice.Detail -
 Stainless Steel Water Pumps: Quality and DurabilityWhen it comes to choosing a water pump, the stainless steel water pump price is a crucial factor.Detail
Stainless Steel Water Pumps: Quality and DurabilityWhen it comes to choosing a water pump, the stainless steel water pump price is a crucial factor.Detail
