Aug . 09, 2024 01:20 Back to list
Exploring the Benefits and Applications of a Three-Phase Submersible Pump for Efficient Water Management
Understanding 3% Phase Submersible Pumps A Comprehensive Overview
Submersible pumps are essential components in various industries, ranging from agriculture to construction, and from wastewater management to oil extraction. Among the various types of submersible pumps, the 3% phase submersible pump stands out due to its specific applications and advantages. This article will delve into what a 3% phase submersible pump is, its working principle, applications, and benefits.
What is a 3% Phase Submersible Pump?
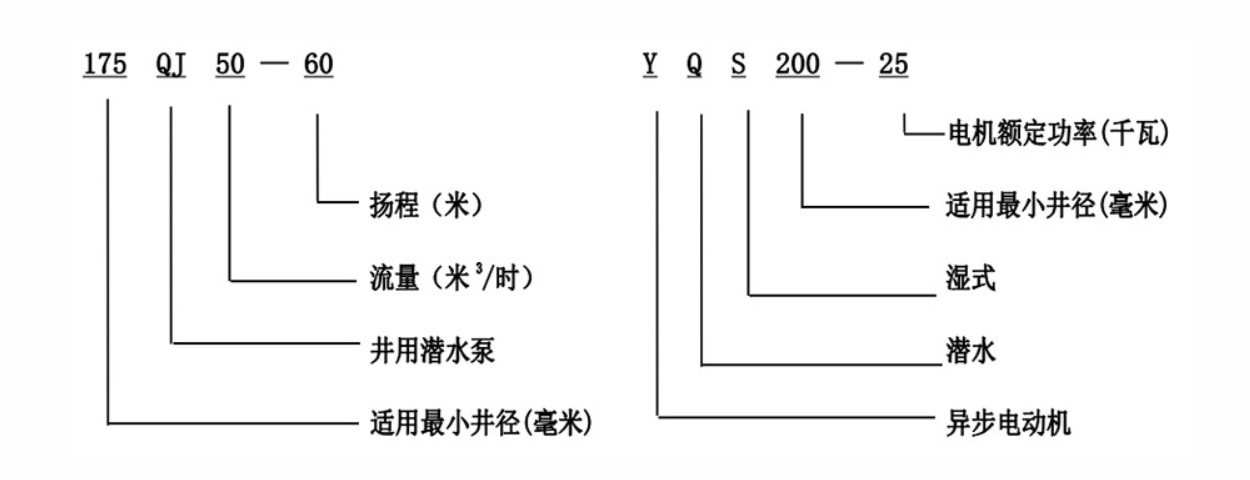
A 3% phase submersible pump is typically designed to work with three-phase power systems, which are common in industrial and agricultural settings. The term 3% refers to the phase configuration rather than the efficiency or performance metrics. In these systems, the pump is submerged in the fluid it is designed to move, allowing for efficient fluid transport without requiring extensive installation of piping and fittings.
The construction of a submersible pump generally includes a motor, impeller, and pump casing. Unlike above-ground pumps, submersible pumps can operate underwater, minimizing the risk of cavitation and allowing for better performance in deep wells or bodies of water.
Working Principle
The operation of a 3% phase submersible pump is based on the principles of fluid dynamics. When the pump is submerged, the motor drives the impeller, which creates a low-pressure zone at the inlet. This pressure differential draws fluid into the pump, where the impeller then expels it with greater pressure into an outlet pipe.
The three-phase power system provides several advantages over single-phase systems. It allows for smoother and more balanced operation, reduces electrical losses, and ensures higher efficiency, particularly when powering large pumps. This configuration is especially beneficial in applications requiring continuous operation over extended periods.
Applications
3% phase submersible pumps are used in various applications, including
3 phase submersible pump
1. Agriculture These pumps are essential for irrigation systems, drawing water from underground aquifers to fields and crops efficiently. 2. Wastewater Management In municipal and industrial wastewater treatment systems, submersible pumps are crucial for moving sewage and effluent to treatment facilities. 3. Mining Operations Submersible pumps are widely used to dewater mines, removing water from pits and enabling safe exploration and extraction of minerals. 4. Oil Extraction In oil fields, these pumps facilitate the extraction of crude oil from underground reservoirs.
Benefits of 3% Phase Submersible Pumps
The advantages of using 3% phase submersible pumps include
- Efficiency The three-phase design allows for higher power and efficiency, especially in larger installations.
- Space-saving Design Being submerged, these pumps occupy less surface space, making them ideal for applications where space is limited.
- Reduced Noise Levels Submersible pumps tend to operate more quietly than surface pumps, making them suitable for residential areas or noise-sensitive environments.
- Durability Constructed for underwater use, these pumps are often built with robust materials that withstand corrosive environments, contributing to longevity and reduced maintenance costs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 3% phase submersible pumps represent a vital technology in various industries, providing efficient and reliable fluid transport solutions. With their unique design and operational advantages, they play an indispensable role in ensuring the effective management of water resources in agricultural, industrial, and municipal applications. Understanding the capabilities and applications of these pumps can help stakeholders make informed decisions about their water management strategies. As technology advances, the efficiency and effectiveness of submersible pumps are expected to continue improving, further solidifying their importance in modern engineering and environmental management.
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
