Jul . 28, 2024 10:21 Back to list
Exploring the Efficiency and Applications of Borehole Pumps in Water Extraction and Supply Systems
Understanding Borehole Pumps An Essential Tool for Water Extraction
Borehole pumps are critical components in the extraction and management of groundwater, especially in areas where surface water is scarce. These pumps are specifically designed to operate in deep wells, typically used for agricultural, industrial, and residential water supply. As the demand for freshwater resources increases, the efficiency and versatility of borehole pumps become ever more important.
What is a Borehole Pump?
A borehole pump is a submersible pump that is installed deep within a borehole, which is a deep, narrow hole drilled into the ground to access underground water reservoirs. These pumps can vary widely in size and capacity, making them suitable for a range of applications from small residential systems to large agricultural irrigation projects. Unlike surface pumps, borehole pumps are designed to withstand the extreme pressure associated with deeper water sources, allowing them to effectively lift water from depths that would be impractical for other pump types.
Types of Borehole Pumps
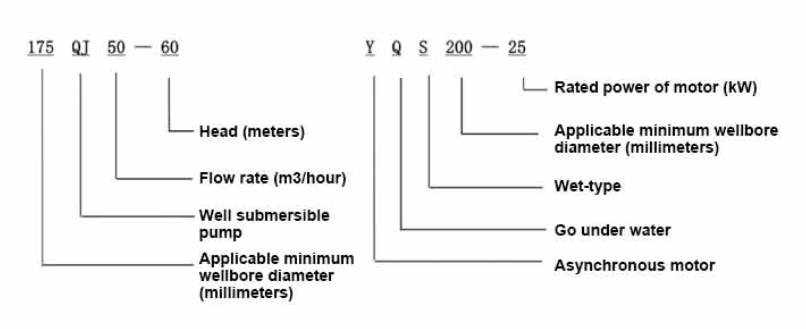
Borehole pumps generally fall into two categories submersible pumps and jet pumps.
1. Submersible Pumps These pumps are submerged in the water they are pumping, which helps to cool the motor and protect it from damage. They are particularly efficient for deep boreholes because they can push water to the surface more effectively than other types. Submersible pumps are often preferable for deeper wells, capable of reaching depths of up to several hundred meters.
2. Jet Pumps While jet pumps can be used to lift water from shallower depths, they operate by creating a vacuum that draws water from the well to the surface. They are typically less efficient than submersible pumps for deep applications but are easier to install and maintain in some cases.
borehole pumps
Applications of Borehole Pumps
Borehole pumps are utilized across various sectors. In agriculture, they provide essential irrigation water, ensuring crops receive adequate moisture in areas where rainfall is insufficient. In domestic settings, borehole pumps supply water for households, particularly in rural areas where municipal water systems may not be available. Additionally, they serve industrial operations that require significant water usage, such as mining and construction.
Advantages of Borehole Pumps
One of the primary benefits of borehole pumps is their ability to extract water from significant depths, making them invaluable in regions with deep aquifers. They also tend to be more energy-efficient than surface pumps, primarily because their operation is less subject to atmospheric pressures. Furthermore, borehole pumps often have a longer lifespan with properly maintained systems, which translates to cost savings over time.
In terms of sustainability, borehole pumps can facilitate better groundwater management. By enabling controlled extraction of water resources, they help prevent issues such as over-extraction and aquifer depletion, especially when integrated with proper monitoring systems that track groundwater levels.
Maintenance and Considerations
While borehole pumps are robust and efficient, they do require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Common maintenance tasks include checking the pump and motor for wear and tear, inspecting electrical connections, and ensuring that the well casing is secure and free from contaminants. Additionally, water quality tests should be conducted regularly to assess any changes in the groundwater and to avoid damage to the pump from sediments or corrosive elements.
In conclusion, borehole pumps play an essential role in modern water extraction practices. Whether for agricultural irrigation, industrial use, or residential supply, these pumps help meet the growing demand for freshwater resources. As global water scarcity becomes a pressing issue, the efficiency and reliability of borehole pumps will continue to be vital for sustainable water management efforts.
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
