Sep . 03, 2024 22:53 Back to list
how does a deep well submersible pump work
How Does a Deep Well Submersible Pump Work?
A deep well submersible pump is an essential device used for extracting water from deep underground sources. These pumps are commonly employed in agricultural irrigation, municipal water supply, and even residential applications to draw water from wells that can reach depths of 300 feet or more. Understanding how a submersible pump operates sheds light on its functionality and efficiency in groundwater extraction.
At its core, a deep well submersible pump consists of two primary components the pump body and the motor. Unlike traditional pumps that are positioned above the water source, submersible pumps are designed to be submerged in the water they are pumping. This unique placement helps to prevent issues associated with cavitation, where vapor bubbles form and collapse, potentially damaging the pump.
How Does a Deep Well Submersible Pump Work?
The water enters the pump through intake screens located at the base. As it is drawn in, the impeller imparts kinetic energy to the water, converting it into pressure energy. This process continues as the water travels through a series of diffusers, which are stationary components designed to slow down the water flow and convert its velocity into pressure. The combined action of the impeller and the diffusers efficiently elevates the water to the surface.
how does a deep well submersible pump work
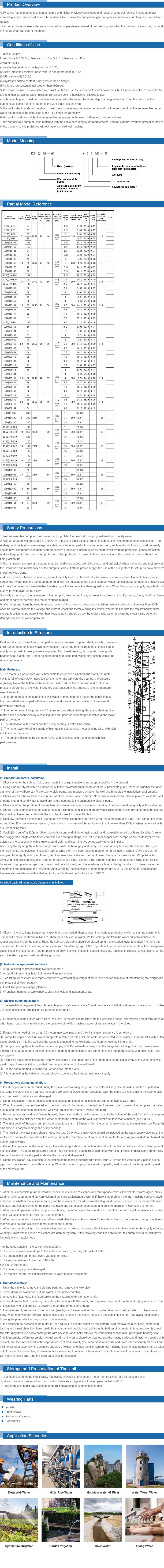
One of the significant advantages of submersible pumps is their ability to handle high water pressure. The deeper the well, the higher the pressure required to reach the surface, and submersible pumps are specifically engineered to function under such conditions. Additionally, these pumps operate quietly since they are submerged, making them suitable for residential areas where noise may be a concern.
Control systems play a vital role in the operation of deep well submersible pumps. These pumps often rely on float switches or pressure sensors to monitor water levels and maintain consistent operation. When the water level drops below a certain threshold, the pump is activated, and it continues to run until the desired level is reached. This automation not only enhances efficiency but also prevents dry running, which could damage the pump.
Maintenance of submersible pumps is important to ensure longevity and reliability. Regular inspections can help identify potential issues, such as wear on the impeller or blockages in the intake screens. Additionally, it is crucial to periodically check the motor and electrical components for any signs of corrosion or wear.
In summary, a deep well submersible pump is a powerful and efficient tool for extracting groundwater from significant depths. Its design, with a motor located within the well, and its use of centrifugal force allow for effective water movement under high pressure. With proper maintenance and monitoring, these pumps provide a reliable source of water for various applications, contributing significantly to water supply systems worldwide.
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
