Nov . 09, 2024 10:28 Back to list
Methods for Evaluating the Performance of Submersible Water Well Pumps
How to Test a Submersible Water Well Pump
A submersible water well pump is an essential component for accessing groundwater, providing homes and farms with a reliable supply of water. Over time, these pumps may experience performance issues, leading to a decrease in water pressure or other operational problems. Testing a submersible water well pump is crucial to ensure it is functioning correctly and efficiently. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to test your submersible water well pump effectively.
Safety First
Before you begin testing your pump, safety should be your top priority. Make sure to turn off the power supply to the pump. This can often be done by switching off the circuit breaker dedicated to the well system. Wearing proper safety gear, such as gloves and safety goggles, can also protect you from potential hazards while inspecting the equipment.
Visual Inspection
Start with a thorough visual inspection of the pump and its components. Look for any signs of wear and tear, corrosion, or damage to the housing and electrical connections. Check the discharge pipe for leaks or cracks that could affect the pump’s performance. Ensure that the pressure tank (if installed) is functioning correctly and does not have any visible leakages.
Measuring Voltage and Current
Using a multimeter, check the voltage and current going to the pump. This will help you identify if there is an electrical issue affecting the pump’s performance. The voltage should match the specifications provided by the manufacturer. If the voltage is too low or fluctuating, it may not be delivering sufficient power to the pump. Additionally, measure the current draw of the pump when it is operational. If the current is significantly higher than the rated value, it may indicate that the pump is overworking or has an internal fault.
Flow Rate Test
how to test a submersible water well pump
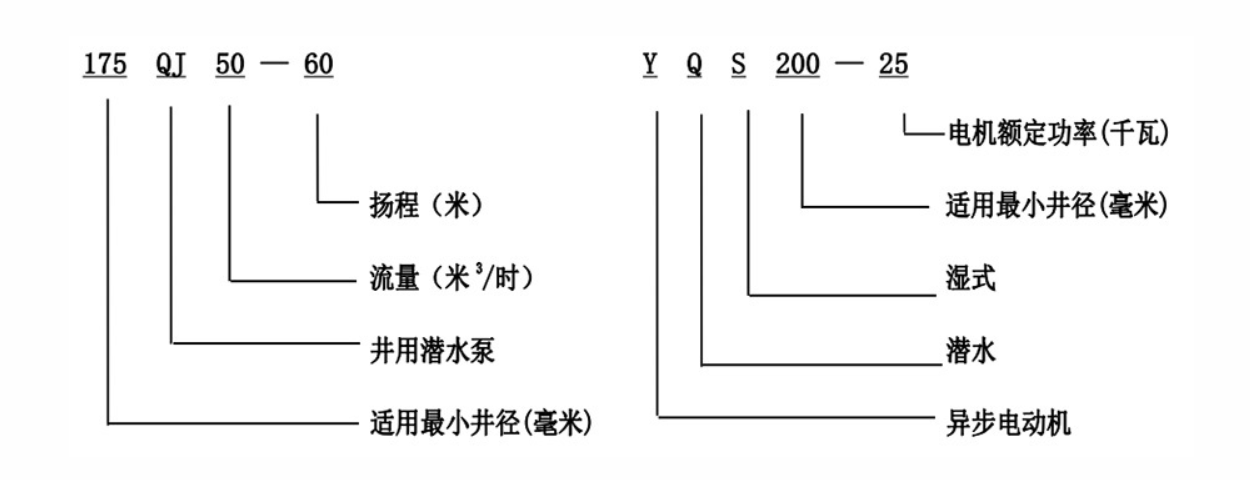
One of the most important aspects of testing a submersible well pump is evaluating its flow rate. This can be accomplished by measuring the amount of water the pump can deliver over a specific period. To perform this test
1. Find a reliable method to collect water, such as a large container (preferably one with marked gallon increments). 2. Turn on the pump and allow it to run for a designated time, typically a few minutes. 3. Measure the volume of water collected during that time. 4. Calculate the flow rate in gallons per minute (GPM) by dividing the total gallons collected by the time in minutes.
Compare the obtained flow rate with the manufacturer’s specifications. If the flow rate is significantly lower, it indicates that the pump may need servicing or replacement.
Checking Pressure
If your system includes a pressure gauge, check the pressure readings while the pump is operating. Proper pressure readings ensure that water is being delivered efficiently throughout your plumbing system. Again, compare your readings to the specifications set by the manufacturer. If the pressure is too low, it could be a sign of a malfunctioning pump or issues in the plumbing system.
Inspecting the Control Box
The control box is a vital component that manages the electrical supply to the pump. Inspect it for any signs of burning, corrosion, or loose wires. If you notice any damage, contact a professional for further diagnosis or replacement.
Conclusion
Testing a submersible water well pump is an essential routine maintenance task that can save you time and money in the long run. By conducting regular inspections and tests, you can detect potential problems early, ensuring that you have a reliable water supply. Remember, if at any point you feel unsure about performing these tests or if the pump exhibits serious issues, it is best to consult a professional technician. Proper maintenance and timely intervention are key to extending the lifespan and efficacy of your submersible water well pump.
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
