Dec . 12, 2024 15:47 Back to list
oil filled vs water filled submersible pump
Oil-Filled vs. Water-Filled Submersible Pumps A Comprehensive Overview
When it comes to choosing a submersible pump for various applications, two common types often come into consideration oil-filled and water-filled pumps. Each design has distinct characteristics that cater to different operational needs, making it essential to understand their similarities and differences when selecting the right pump for your project.
Understanding Submersible Pumps
Submersible pumps are designed to operate while submerged in the fluid they are pumping. Unlike surface pumps, which draw water into the system, submersible pumps are placed directly in the liquid reservoir, allowing for more efficient operation, especially in deep water applications. These pumps are commonly used in sewage systems, water wells, industrial applications, and agricultural irrigation.
Oil-Filled Submersible Pumps
Oil-filled submersible pumps are equipped with a sealed motor that is submerged in an oil-filled housing. The oil serves multiple purposes it lubricates the motor, dissipates heat, and protects the motor components from the surrounding fluid.
Advantages of Oil-Filled Pumps
1. Heat Dissipation The oil assists in absorbing and distributing the heat generated by the motor during operation. This feature increases the lifespan of the pump, particularly in high-demand environments. 2. Reduced Risk of Contamination The oil barrier helps prevent the ingress of contaminants into the motor compartment, thus reducing the risk of corrosion and wear.
3. Higher Efficiency Oil-filled pumps tend to be more energy-efficient than their water-filled counterparts, allowing for longer operational periods without overheating.
Disadvantages of Oil-Filled Pumps
1. Maintenance Challenges If a leak occurs, it can lead to oil contamination of the fluid being pumped, which may not be acceptable in certain applications, such as drinking water. Regular checks are necessary to ensure that the seals are intact.
2. Cost Typically, oil-filled pumps are more expensive due to their complex construction and the need for additional components.
3. Weight and Size These pumps can be bulkier and heavier, which may affect installation and maneuverability in some situations.
oil filled vs water filled submersible pump
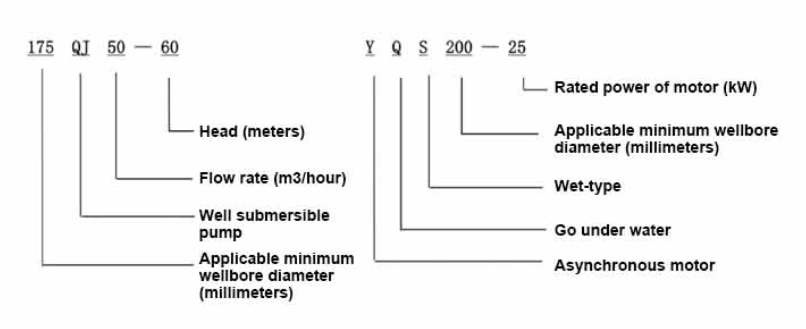
Water-Filled Submersible Pumps
Water-filled submersible pumps, on the other hand, utilize the liquid they are pumping for cooling and lubrication. The motor is directly exposed to the water, and while this can lead to certain efficiencies, it comes with its own set of challenges.
Advantages of Water-Filled Pumps
1. Simplicity and Cost Water-filled pumps generally have a simpler design, making them less expensive and easier to manufacture. This often translates to lower purchase costs for the end user.
2. Lightweight These pumps are typically lighter and more compact, making them easier to transport and install in various settings.
3. Environmentally Friendly There is no risk of oil contamination, making water-filled pumps suitable for applications involving potable water or environmentally sensitive areas.
Disadvantages of Water-Filled Pumps
1. Heat Management Because they rely on the pumped liquid for cooling, they can overheat if the surrounding water temperatures increase or if the pump runs dry.
2. Limited Lifespan The exposure of the motor to water can increase the likelihood of corrosion and wear over time, potentially shortening the lifespan of the pump.
3. Efficiency at Depth The performance of water-filled pumps can decrease at considerable depths, which may limit their use in deep well applications compared to oil-filled models.
Conclusion
In summary, both oil-filled and water-filled submersible pumps have their respective advantages and disadvantages. The decision on which type to use largely depends on the specific application and operational environment. For projects requiring high efficiency and where temperature management is crucial, oil-filled pumps may be the better choice. Conversely, for applications where cost, simplicity, and environmental considerations are paramount, water-filled pumps often present a more suitable alternative.
When selecting a submersible pump, it is essential to evaluate the specific needs of your project, including fluid type, depth of application, and budgetary constraints, to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the equipment.
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
