Dec . 11, 2024 22:18 Back to list
pump submersible
The Versatility of Submersible Pumps in Modern Applications
Submersible pumps have become integral to various industries due to their efficiency and versatility. Designed to operate while submerged in liquid, these pumps differ significantly from traditional pumps. They are hermetically sealed and equipped with a motor that pushes fluids to the surface rather than sucking them up, making them ideal for numerous applications.
Principle of Operation
At the heart of a submersible pump’s efficiency is its unique working principle. The motor is located below the fluid’s surface, encouraging a compact design that reduces leakage risks and mechanical wear. The pump harnesses the pressure created by the fluid itself, allowing it to push water, sewage, or other fluids upwards through the discharge pipe. This design not only ensures smooth operation but also minimizes the risk of cavitation, a common problem in surface pumps.
Applications in Various Industries
1. Wastewater Management One of the most critical uses of submersible pumps is in wastewater and sewage applications. These pumps are typically used in treatment plants and septic systems to transport sewage away from homes and businesses. Their ability to handle solids and large volumes of fluid makes them invaluable in municipal wastewater systems, where they help maintain sanitation and environmental safety.
2. Agriculture Agriculture heavily relies on submersible pumps for irrigation purposes. Whether extracting groundwater from wells or distributing water from underground reservoirs, these pumps ensure efficient water delivery to crops. Their durability in sandy or muddy environments, combined with the ability to maintain a consistent flow, is essential for maximizing agricultural yields.
3. Construction and Draining In construction, managing water effectively is crucial. Submersible pumps are employed for dewatering sites, such as foundations or excavations, to prevent water accumulation during rainy seasons. Their portability and ability to work in confined spaces make them a preferred choice for construction companies aiming to keep sites dry and safe.
4. Mining and Oil Extraction The mining industry also benefits from submersible pumps, particularly in hydraulic mining operations. These pumps can efficiently transfer water mixed with ore, thereby facilitating ore recovery. Similarly, in oil extraction, submersible pumps help in moving crude oil from deep underground reservoirs to the surface with minimal energy consumption.
pump submersible
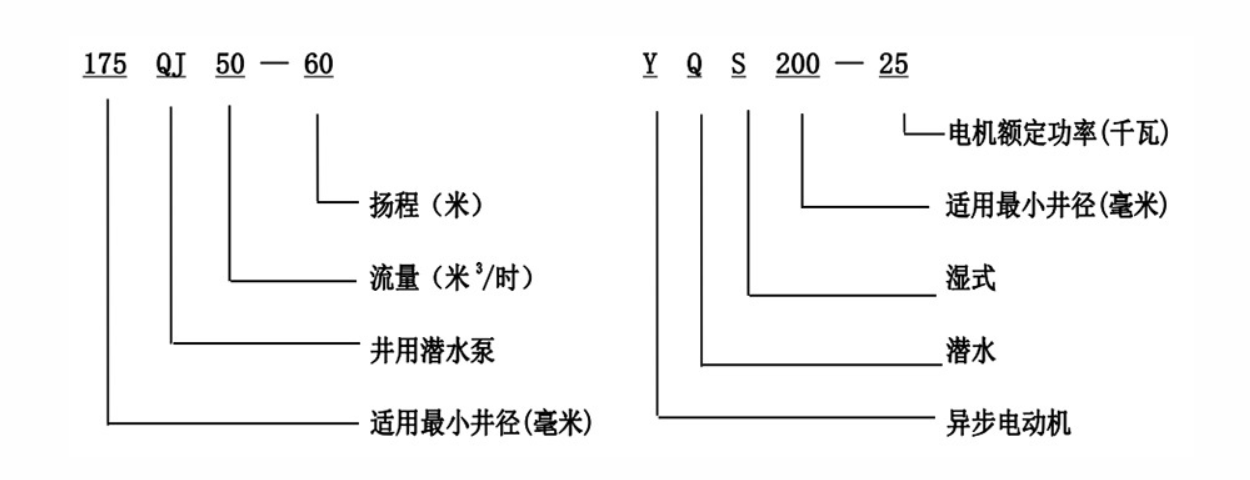
Advantages of Submersible Pumps
One of the significant advantages of submersible pumps is their energy efficiency. By pushing fluid rather than pulling it, they typically require less energy, which translates into lower operational costs. Additionally, these pumps often come with a longer lifespan due to reduced wear and tear from operating below the fluid level.
Their compact design also contributes to space-saving benefits. Because submersible pumps can work in smaller spaces without additional equipment, they are often seen as a perfect solution for tight installations.
Innovation and Future Prospects
The submersible pump industry is witnessing continuous advancements. Innovations in materials, technology, and design are leading to the development of more efficient and durable pumps. Smart technology integration, such as remote monitoring and automated controls, is transforming how these pumps operate, allowing for predictive maintenance and improved efficiency.
As concerns around water resource management and environmental sustainability grow, the importance of submersible pumps is likely to increase. More industries will rely on these pumps not only for efficiency but also to contribute to sustainable practices.
Conclusion
In summary, submersible pumps are essential devices that support various sectors through their versatile applications and energy-efficient operation. From managing wastewater to bolstering agricultural productivity, their significance cannot be overstated. As technology advances, submersible pumps will continue to play a crucial role in meeting the world's increasing demands for water management and sustainability solutions.
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
