Nov . 23, 2024 14:27 Back to list
sewage submersible pump
Understanding Sewage Submersible Pumps Essential for Modern Waste Management
Sewage submersible pumps play an integral role in modern waste management systems, effectively facilitating the transport of wastewater and sewage from lower to higher elevations. These pumps are specifically designed to operate underwater, making them ideal for various applications where traditional pumps cannot be effectively utilized.
What is a Sewage Submersible Pump?
A sewage submersible pump is designed to be submerged in a fluid, allowing it to pump sewage and other wastewater materials directly from the source to a different location, such as a treatment facility or a septic tank. Unlike surface pumps that draw fluids through suction, submersible pumps are equipped with a sealed motor that is submerged beneath the liquid being pumped. This design minimizes the risk of any air getting trapped in the system, which helps maintain the efficiency of the pump.
Key Features and Working Principles
1. Design and Construction Sewage submersible pumps are made with robust materials to withstand harsh conditions. Typically manufactured from stainless steel or cast iron, these pumps resist corrosion and wear from abrasive solids in wastewater. The impeller, an essential component that moves the water, is designed to handle solids and debris efficiently.
2. Operational Efficiency The pump operates when the float switch detects a certain water level. When activated, the pump pushes sewage upwards through a discharge pipe. The high-performance motor can handle solids up to a specified diameter, thus ensuring that clogs are minimized.
3. Energy Efficiency Many modern submersible pumps come equipped with variable speed drives. This technology allows the pump to adjust its flow rate based on the volume of sewage, thus optimizing energy consumption. In urban areas where wastewater flow can fluctuate, this feature becomes crucial for reducing operational costs.
Applications of Sewage Submersible Pumps
Sewage submersible pumps are utilized in a variety of applications, including
- Residential Wastewater Systems Homeowners often use these pumps in basements or areas prone to flooding where sewage must be transported to a municipal sewer system or septic tank. - Industrial Applications Factories and manufacturing plants utilize submersible pumps for managing wastewater in production processes, ensuring clean operations.
sewage submersible pump
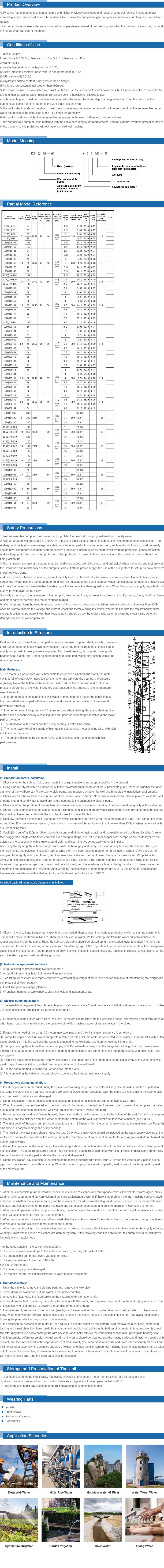
- Municipal Wastewater Management Cities rely on these pumps in lift stations to transport sewage from lower areas to treatment facilities, thus forming a critical part of infrastructure
.- Construction Sites During construction, these pumps can quickly remove groundwater or sewage accumulating around the site, ensuring safe and efficient work conditions.
Benefits of Sewage Submersible Pumps
1. Space Saving Since these pumps are submerged, they do not occupy above-ground space, making them suitable for limited areas.
2. Reduced Noise Levels Operating underwater minimizes noise pollution, which is beneficial for residential and urban environments.
3. Enhanced Durability The robust construction allows these pumps to withstand tough conditions, reducing maintenance efforts and costs.
4. Versatility These pumps can handle a variety of fluids, making them suitable for both sewage and other types of wastewater.
Conclusion
Sewage submersible pumps are undeniably essential in modern waste management. Their ability to efficiently transport sewage and handle solids makes them vital for a range of applications, from residential settings to industrial landscapes. As we move towards more advanced waste management solutions, the technology behind these pumps continues to evolve, emphasizing energy efficiency and reliability.
Investing in a high-quality sewage submersible pump not only ensures effective wastewater management but also contributes to a cleaner and more sustainable environment. With increasing urbanization and industrial growth, the importance and functionality of these pumps will continue to grow, solidifying their role as a cornerstone in waste management systems across the globe.
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
