Nov . 10, 2024 12:10 Back to list
Exploring the Benefits and Applications of Submersible Oil Pump Technology in Modern Industries
Submersible Oil Pumps An Overview
Submersible oil pumps are specialized devices designed to lift hydrocarbons from underground reservoirs and deliver them to the surface, where they can be processed and refined. They have significant applications in the oil and gas industry, particularly in areas where conventional pump systems may fail to operate efficiently due to depth or environmental conditions.
Working Principle
The submersible oil pump operates under a simple yet effective principle. It consists of a motor and a pump assembly that are both submerged in the fluid being pumped. The motor is hermetically sealed to prevent any oil from entering the electrical components, ensuring their safety and operational reliability. When powered, the motor turns the pump impeller, creating a pressure difference that moves the fluid upward through a pipe to the surface.
One of the primary advantages of submersible pumps is their ability to operate at considerable depths. This is particularly useful in deep-well oil extraction, where the pressure at the bottom of the well could be too great for surface pumps to overcome. By submerging the pump, operators can effectively manage these pressures and enhance the overall efficiency of the pumping system.
Types of Submersible Oil Pumps
There are various types of submersible oil pumps available, each designed for specific applications
1. Centrifugal Pumps The most common type used in the oil industry, these pumps use rotational energy to move oil. They are efficient for continuous flow applications, making them suitable for conventional oil extraction.
2. Positive Displacement Pumps These are utilized in circumstances where precise volumes of fluid need to be pumped or where high viscosity fluids are present. They operate by trapping a fixed amount of fluid and forcing it through the discharge.
3. Progressing Cavity Pumps Often used for heavy crude oil extraction, these pumps have a helical rotor that moves the oil through a stator, providing high efficiency even in challenging conditions.
Advantages
submersible oil pumps
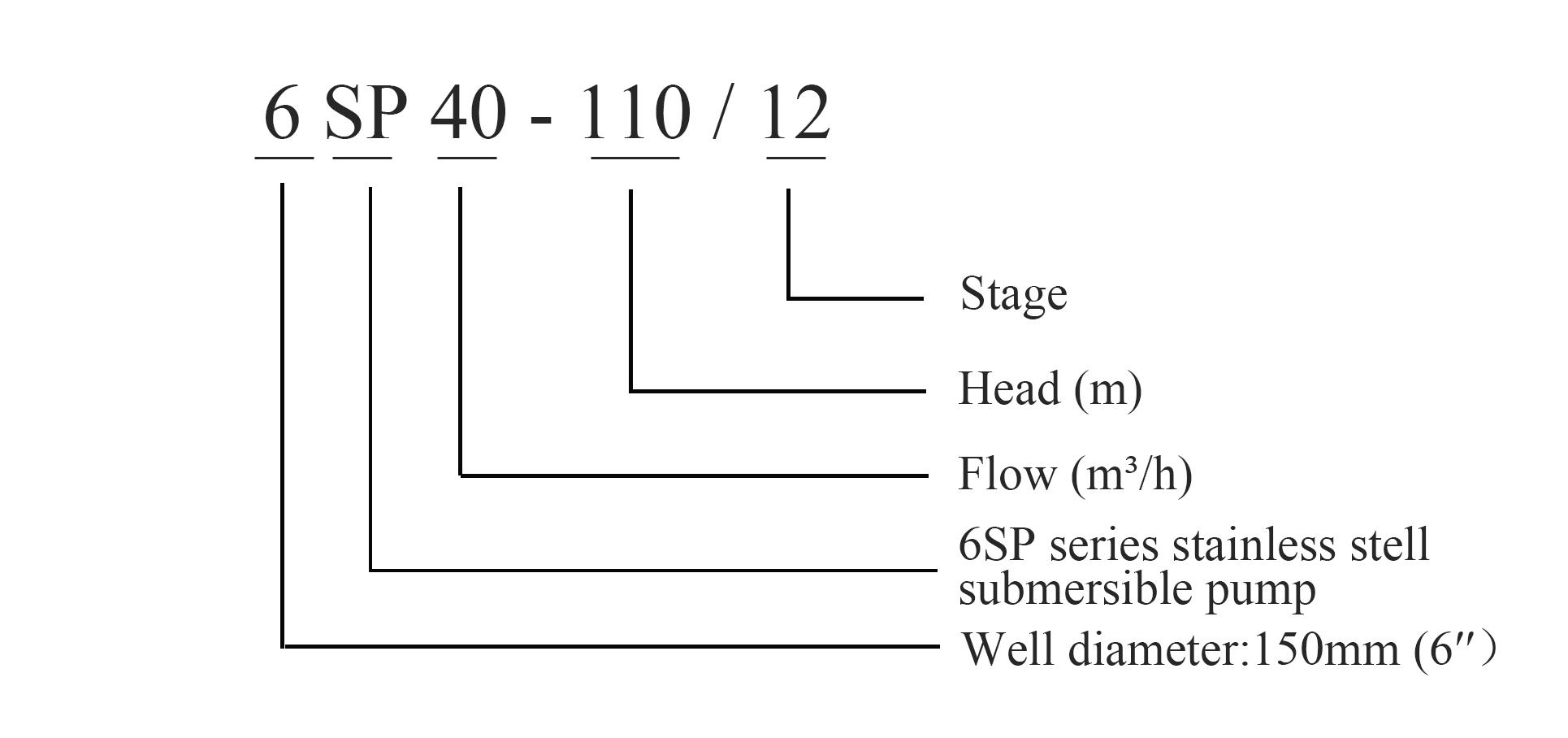
Submersible oil pumps offer several benefits
- High Efficiency By operating underwater, these pumps can take advantage of hydrostatic pressure to aid in fluid movement, which can reduce energy consumption.
- Reduced Surface Footprint Submersible pumps eliminate the need for extensive surface infrastructure, allowing for more compact setups that can be operated in environmentally sensitive areas.
- Ease of Maintenance Many submersible pumps are designed for easy retrieval for maintenance and repairs, minimizing downtime
.Challenges
Despite their advantages, submersible oil pumps also face some challenges
- Corrosion Continuous exposure to harsh chemicals and high pressures can lead to wear and corrosion. Selecting the right materials for construction is crucial to extend the life of the equipment.
- Heat Management Since these pumps are submerged, heat dissipation can be a concern. Operators must ensure that the motor does not overheat to maintain efficiency.
- Transport and Installation Submersible pumps can be heavier and more complicated to transport and install compared to other types of pumps, which could result in increased logistical costs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, submersible oil pumps play a critical role in modern oil extraction processes. Their ability to operate efficiently at significant depths and in challenging conditions highlights their importance in the industry. As technology continues to advance, the design and efficiency of submersible pumps are likely to improve, further solidifying their role in the sustainable exploitation of oil resources across the globe. With ongoing research and development, these pumps will play a crucial role in addressing the world's increasing energy demands while minimizing environmental impacts.
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
