Oct . 03, 2024 22:48 Back to list
submersible pumps
Submersible pumps are essential tools used across various industries and applications for efficient fluid transfer and management. Designed to function submerged in fluid, these pumps offer numerous advantages over traditional pumps, making them a popular choice for wastewater management, irrigation, and even oil extraction.
The operating principle of submersible pumps is relatively straightforward. These pumps are hermetically sealed, preventing water ingress into the motor components. This design allows them to be placed directly in the fluid they are pumping, which eliminates the need for priming and reduces the risk of cavitation. When submerged, the pump impeller creates a pressure differential, facilitating the movement of the fluid up through the pump and out of the discharge outlet.
One of the major benefits of submersible pumps is their versatility. They come in various sizes and designs to accommodate different fluid types and flow rates. For instance, submersible sewage pumps are specifically designed to handle wastewater that may contain solids, while submersible well pumps are utilized to extract groundwater from deep wells. This adaptability makes them invaluable in agricultural applications, where they are used for irrigation, as well as in municipal applications for sewage and stormwater management.
Moreover, submersible pumps are known for their energy efficiency. By being submerged, they lower the overall energy costs associated with pumping due to minimized friction losses. This not only enhances performance but also leads to lower operational costs, especially in applications where the pumps are running continuously, such as in drainage systems or fish farming.
submersible pumps
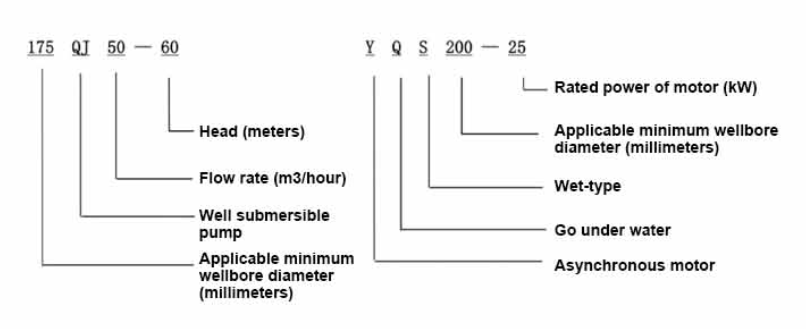
Technological advancements have also improved the functionality of submersible pumps. Modern pumps often incorporate smart technology, allowing for remote monitoring and control. This feature enhances operational reliability, enabling users to track performance metrics and receive alerts for maintenance needs or operational anomalies. As a result, businesses can minimize downtime and ensure efficient fluid management.
However, it is essential to consider maintenance when utilizing submersible pumps. Although they are designed for durability, regular checks on seals, bearings, and electrical connections are necessary to prolong their lifespan and ensure optimal performance. Depending on the application, sediment build-up and other debris might require periodic cleaning to prevent clogs and maintain effective operation.
In summary, submersible pumps are critical components in various sectors, contributing to efficient fluid management and operational efficiency. Their design, versatility, and energy-saving features make them an excellent choice for numerous applications. With ongoing technological advancements, submersible pumps will continue to evolve and enhance their effectiveness in the face of growing industrial and environmental challenges.
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
