Nov . 16, 2024 23:07 Back to list
submersible pumps for wells
Submersible Pumps for Wells An Essential Tool for Efficient Water Extraction
Submersible pumps are an indispensable resource in various applications, particularly in agriculture, municipal water supply, and residential water systems. Specifically designed to operate underwater, these pumps are engineered to efficiently extract water from wells, ensuring a steady supply for irrigation, drinking, and industrial use. In this article, we will explore the workings, benefits, and selection criteria of submersible pumps for wells.
How Submersible Pumps Work
Unlike conventional pumps that are mounted above water sources, submersible pumps are placed directly into the water. They consist of a sealed motor coupled to a pump body, which is submerged below the water level. The motor drives an impeller that creates suction, drawing water into the pump and pushing it to the surface through a discharge pipe. This unique design allows submersible pumps to operate more efficiently since they do not need to overcome the gravitational pull of the water column during operation.
The operating principle is anchored in the pump’s ability to prevent cavitation, a phenomenon that occurs when the pressure of the fluid drops below its vapor pressure, leading to the formation of vapor bubbles. Because submersible pumps are submerged in liquid, they maintain adequate pressure around the impeller, thus significantly reducing the chances of cavitation and ensuring longevity.
Advantages of Submersible Pumps
1. Efficiency One of the most significant advantages of submersible pumps is their high efficiency. These pumps are designed to handle large volumes of water with minimal energy consumption, making them ideal for applications requiring consistent performance over extended periods.
2. Space-saving Design Since submersible pumps are installed underground, they do not occupy space above ground. This is particularly beneficial in residential setups where outdoor space may be limited.
3. Reduced Risk of Contamination Submersible pumps are situated below the water level, which mitigates the risk of contamination from surface debris, pests, and environmental pollutants. This is crucial for maintaining the purity of drinking water sources.
4. Less Noise Because the pump is submerged, operational noise is significantly reduced, making submersible pumps a quieter alternative to surface pumps.
submersible pumps for wells
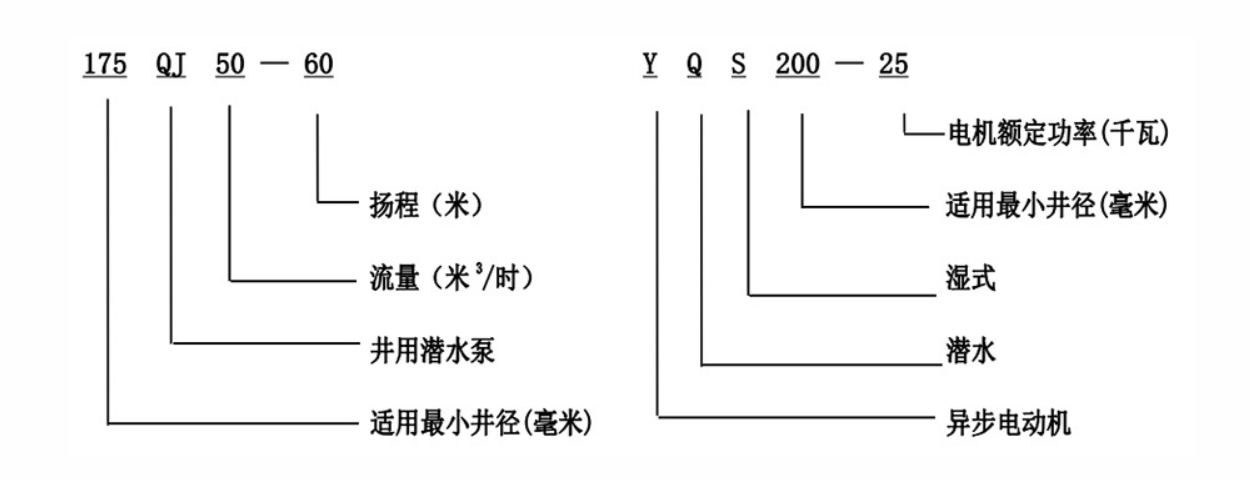
Choosing the Right Submersible Pump
Selecting the right submersible pump involves considering several critical factors
1. Well Depth It is essential to know the depth of the well, as it directly impacts the pump's performance. Manufacturers typically provide specifications indicating the maximum pumping depth.
2. Flow Rate Determine the necessary flow rate for your application. This measurement, expressed in gallons per minute (GPM), reflects how quickly the pump can deliver water from the well.
3. Water Quality Assess the quality of water; if it contains sediment or debris, a pump with a proper filtering system should be selected to prevent damage.
4. Power Supply Ensure that the power supply is compatible with the pump’s requirements. Pumps can operate on electricity, solar power, or generators based on the site’s infrastructure.
5. Material Construction Pumps made from corrosion-resistant materials are preferable, especially in applications involving brackish or saline water.
Conclusion
Submersible pumps for wells play a vital role in providing reliable access to water in numerous sectors. Their efficiency, compact design, and environmental advantages make them a preferred choice for many applications. By understanding how these pumps work and their advantages, users can make informed decisions when selecting the right pump for their needs. With the right submersible pump, optimal water extraction can be achieved, ensuring a consistent and safe water supply for various uses.
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
