Nov . 26, 2024 05:22 Back to list
submersible tank pump
Understanding Submersible Tank Pumps
Submersible tank pumps have become an essential piece of equipment in various industries due to their effectiveness in transporting fluids from below ground levels to the surface. These pumps are designed to operate underwater, making them ideal for applications that involve pumping water from wells, ponds, or tanks. This article aims to explore the features, advantages, applications, and maintenance of submersible tank pumps.
Features and Design
Submersible tank pumps are characterized by their unique design, which allows them to be fully submerged in the liquid they are pumping. This design typically consists of a sealed motor that prevents water entry, a pump housing, and an impeller. The motor drives the impeller, creating suction that draws fluid into the pump and pushes it to the surface through a discharge pipe.
The construction materials of submersible pumps are crucial for their longevity and efficiency. Many are made from corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel or thermoplastic to withstand harsh environments. Additionally, the compact design of these pumps allows for easy installation in various locations, including tight spaces where traditional pumps may not fit.
Advantages
One of the most significant advantages of submersible tank pumps is their efficiency. By being submerged, these pumps are less susceptible to cavitation, a common problem in above-ground pumps that can lead to damage and decreased performance. Submersible pumps can effectively handle solids and slurries, making them suitable for wastewater and sewage applications.
Another advantage is the reduction in noise pollution. Since the pump operates underwater, it generates significantly less noise than surface pumps. This feature is particularly desirable in residential areas or quiet environments where noise levels need to be kept to a minimum.
Moreover, submersible tank pumps are often more energy-efficient. Their design allows them to operate at lower power levels while still delivering high performance. This efficiency can lead to lower operational costs over time, making them a cost-effective solution for many applications.
submersible tank pump
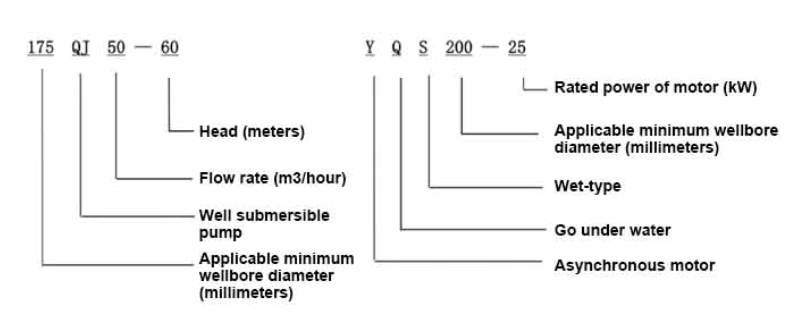
Applications
Submersible tank pumps find a wide range of applications across various industries. In residential settings, they are commonly used for dewatering basements, managing groundwater levels, and draining swimming pools. In agriculture, these pumps facilitate irrigation systems and drainage of fields.
In industrial applications, submersible pumps are crucial for transferring chemicals, slurries, and wastewater. They are extensively used in mining operations for dewatering purposes and in construction sites for managing water accumulation. Additionally, these pumps play a vital role in aquaculture for water movement and aeration.
Maintenance
Proper maintenance of submersible tank pumps is essential for ensuring their longevity and reliability. Regular inspections should be conducted to check for wear and tear, especially on the seals and impellers. It is also important to keep the pump clean and free from debris that could clog the intake.
Routine servicing, including changing the oil in oil-filled pumps and ensuring electrical connections are robust, can prevent failures and prolong operational life. If the pump shows signs of inefficiency, professional servicing may be necessary to address any underlying issues.
Conclusion
Submersible tank pumps provide a reliable and efficient solution for a variety of fluid transport needs. Their unique design, energy efficiency, and versatility in applications make them a popular choice across residential, agricultural, and industrial sectors. By understanding their features and ensuring proper maintenance, users can maximize their performance and extend their lifespan, thus making a smart investment for their fluid management needs.
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
