Nov . 12, 2024 21:18 Back to list
submersible turbine pump
The Submersible Turbine Pump An Essential Tool for Modern Water Management
In the realm of water management, the submersible turbine pump (STP) stands as a pivotal technology that ensures efficient and reliable water extraction for various applications. Whether in agricultural irrigation, municipal water supply, or industrial processes, these pumps provide a vital solution to meet the increasing global water demands.
Understanding Submersible Turbine Pumps
A submersible turbine pump is a type of rotating pump that is placed underwater, often used to draw groundwater from deep wells. Unlike surface pumps, which are located above the ground and require a suction lift to function, submersible pumps operate submerged in the fluid being pumped. This design allows them to push water to the surface, making them particularly effective for deep well installations.
The construction of an STP consists of several key components a motor, impellers, and a discharge head. The motor, designed to be waterproof, is typically located at the bottom of the pump assembly, close to the impellers, which consist of multiple stages to increase water pressure as it rises through the pump. As water enters, the impellers rotate, imparting kinetic energy that propels the water upwards through a series of stages to the surface.
Advantages of Submersible Turbine Pumps
The efficiency of submersible turbine pumps offers numerous benefits. One of the primary advantages is their ability to operate at great depths, making them suitable for extracting water from aquifers that are not accessible using traditional pumps. Their submerged operation minimizes the risk of cavitation, a phenomenon that can damage pump components and reduce efficiency.
Moreover, STPs have a smaller surface footprint compared to above-ground pumps, which makes them ideal for installations in locations where space is limited. Their robust design and durability also contribute to lower maintenance costs over time. Submersible pumps generally have longer lifespans due to fewer components exposed to potential damage from environmental factors.
Applications in Various Sectors
submersible turbine pump
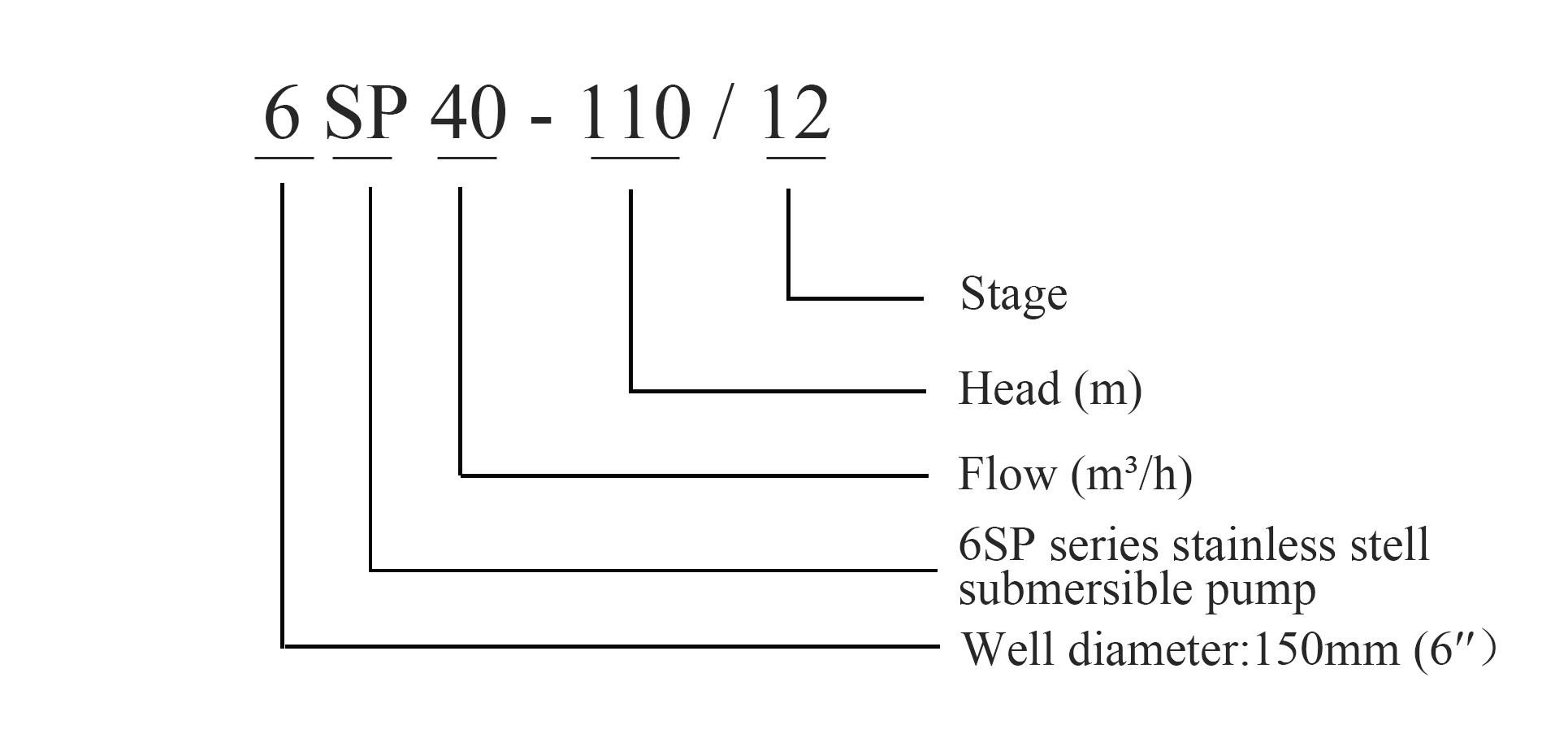
The applications of submersible turbine pumps are vast and varied. In agriculture, they play a crucial role in irrigating crops by drawing groundwater efficiently from deep wells. This usage is particularly important in arid regions where surface water is scarce, helping farmers maintain productivity and sustainability.
Municipal water utilities also rely on STPs for supplying drinking water. These pumps are essential for efficiently accessing groundwater resources and often play a vital role in community resilience against droughts and water shortages.
In the industrial sector, submersible pumps are employed in process water applications, wastewater management, and even in mining operations where dewatering is critical. Their ability to handle varying water qualities, including fluids with contaminants or sediment, confirms their versatility across different environments.
Future Trends and Developments
As global water demands continue to escalate due to population growth and climate change, the importance of efficient water extraction technologies like submersible turbine pumps is more relevant than ever. Innovations such as solar-powered submersible pumps are gaining traction, providing sustainable solutions in remote areas where electricity supply is limited.
Furthermore, advances in materials and smart technology are enhancing the design and operational capabilities of STPs. Integrating IoT sensors for real-time monitoring allows for predictive maintenance and optimized performance, ensuring these pumps operate at peak efficiency while minimizing energy consumption.
Conclusion
In summary, submersible turbine pumps are integral to modern water management systems. Their efficiency, reliability, and adaptability make them a go-to option for various applications, from agriculture to municipal water supply and industrial processes. As technologies evolve and water scarcity becomes a more pressing global issue, STPs will undoubtedly continue to play a vital role in sustainable water resource management.
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
