Nov . 27, 2024 11:54 Back to list
Submersible Water Pumps for Efficient and Reliable Underwater Water Management Solutions
Understanding Submersible Water Pumps A Comprehensive Overview
Submersible water pumps play a critical role in various applications, ranging from agricultural irrigation to municipal water supply and groundwater extraction. These pumps are designed to operate when fully submerged in water, making them ideal for a range of environments and conditions. This article delves into the components, working principle, advantages, and common applications of submersible pumps.
Components and Working Principle
A submersible pump consists of several key components that work together to effectively move water from one location to another. The primary parts include
1. Motor Unlike standard pumps, the motor is located below the water surface. It is hermetically sealed to prevent water ingress and is often oil-filled to keep the temperature in check.
2. Pump Body The pump body contains a series of impellers that create the flow of water. These impellers are usually made of durable materials to withstand prolonged exposure to water and potential abrasive elements.
3. Discharge Pipe This component allows the pumped water to exit the pump and flow to the desired location. The discharge is designed to be durable enough to handle the pressure of the water being pushed through.
The operation of submersible pumps is relatively straightforward. When the motor powers the impellers, they rotate and create a low-pressure zone at the inlet. This low pressure draws water into the pump. The impeller’s motion then converts kinetic energy into pressure, pushing the water upwards through the discharge pipe. One of the key features of submersible pumps is that they can handle high head heights, making them suitable for deep wells and other applications where water needs to be lifted considerable distances.
Advantages of Submersible Pumps
Submersible water pumps offer several significant advantages
1. Efficiency As the pumps are designed to work underwater, they do not suffer from the issue of cavitation, which can affect surface pumps. This leads to improved efficiency and lower energy consumption.
2. Space-Saving Design Submersible pumps are compact and take up less surface space, which is particularly beneficial in areas where space is limited.
water pump submersible
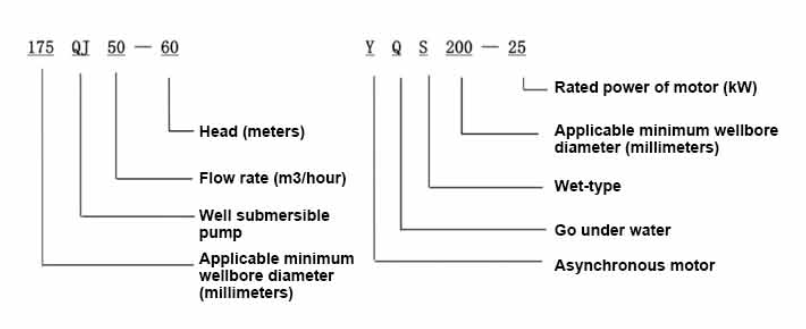
4. Versatility These pumps can be used in various settings, including wells, ponds, and wastewater management systems, demonstrating their adaptability across different situations.
5. Reliability Submersible pumps are generally robust and designed to function consistently over long periods, even in harsh conditions.
Common Applications
Submersible water pumps have a wide range of applications, including
1. Agricultural Use Farmers often use submersible pumps to extract groundwater for irrigation, especially in regions where surface water sources are scarce.
2. Residential Applications Homeowners utilize these pumps for draining flooded basements, removing unwanted water from yards, and for home wells.
3. Municipal Water Supply Many cities rely on submersible pumps to draw freshwater from underground aquifers to supply their water systems.
4. Wastewater Management Submersible pumps are commonly used in treatment plants to move sewage and other wastewater products.
5. Construction and Excavation These pumps help in dewatering construction sites, effectively keeping the area dry and safe for work.
Conclusion
In conclusion, submersible water pumps are an integral part of modern water management and supply systems. Their efficiency, versatility, and compact design make them suitable for various applications, from agriculture to municipal use. Understanding their components and operation is essential for selecting the right pump for specific needs and ensuring effective water management solutions. Whether you are a homeowner, farmer, or professional involved in water management, recognizing the value of submersible pumps can lead to better decision-making and project outcomes.
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
