jan . 16, 2025 04:35 Back to list
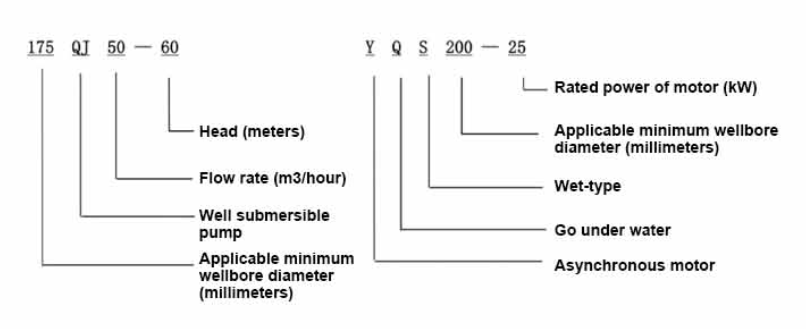
175QJ Deep Well Submersible Pump
Priming a submersible well pump is a crucial process that ensures efficient water delivery, optimal pump performance, and longevity. This step is essential for preventing airlocks and cavitation, which can damage the pump or significantly reduce its efficiency. Here’s an in-depth look at how to prime a submersible well pump, drawing from extensive experience and technical expertise.
4. Monitor Pressure Gauge If your setup includes a pressure gauge switch, monitor it closely. As the pump runs, it should build pressure steadily. Any unusual fluctuations or failure to build pressure requires immediate investigation, possibly indicating trapped air or leaks in the system. 5. Test Run Restore power and initiate a test run of the pump. Observe the water flow for uniformity. If the pump is properly primed, water should flow without interruption. Be ready to switch off the power if you notice any irregularities, such as sputtering, which could indicate air in the system. 6. Perform Ongoing Maintenance Regular maintenance is vital in preventing future priming issues. Routinely check for leaks in discharge lines, inspect electrical components, and ensure the pump is free of sediment and debris. These steps can help avert complications that might necessitate repeated priming. Seeking Expertise and Professional Guidance In complex installations or when persistent issues with priming arise, it might be necessary to seek professional assistance. Specialists in submersible pump systems can offer a depth of knowledge and experience that ensures your well pump operates at peak efficiency. They can also provide insights into the latest technologies and products that may improve system reliability. Conclusion Properly priming a submersible well pump combines precise execution with thorough understanding and regular maintenance practices. This expertise not only enhances the pump's performance but also extends its operational life, ensuring reliable water supply for years. As trusted solutions are tailored and applied, they affirm the authoritative and trustworthy approach required for optimal functionality and customer satisfaction.
4. Monitor Pressure Gauge If your setup includes a pressure gauge switch, monitor it closely. As the pump runs, it should build pressure steadily. Any unusual fluctuations or failure to build pressure requires immediate investigation, possibly indicating trapped air or leaks in the system. 5. Test Run Restore power and initiate a test run of the pump. Observe the water flow for uniformity. If the pump is properly primed, water should flow without interruption. Be ready to switch off the power if you notice any irregularities, such as sputtering, which could indicate air in the system. 6. Perform Ongoing Maintenance Regular maintenance is vital in preventing future priming issues. Routinely check for leaks in discharge lines, inspect electrical components, and ensure the pump is free of sediment and debris. These steps can help avert complications that might necessitate repeated priming. Seeking Expertise and Professional Guidance In complex installations or when persistent issues with priming arise, it might be necessary to seek professional assistance. Specialists in submersible pump systems can offer a depth of knowledge and experience that ensures your well pump operates at peak efficiency. They can also provide insights into the latest technologies and products that may improve system reliability. Conclusion Properly priming a submersible well pump combines precise execution with thorough understanding and regular maintenance practices. This expertise not only enhances the pump's performance but also extends its operational life, ensuring reliable water supply for years. As trusted solutions are tailored and applied, they affirm the authoritative and trustworthy approach required for optimal functionality and customer satisfaction.
Latest news
-
Water Pumps: Solutions for Every Need
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Submersible Well Pumps: Reliable Water Solutions
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Stainless Steel Water Pumps: Quality and Durability
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Powerful Water Pumps: Your Solution for Efficient Water Management
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Oil vs Water Filled Submersible Pumps: Which is Better?
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Deep Well Pumps: Power and Reliability
NewsJul.30,2025
-
 Water Pumps: Solutions for Every NeedWhen it comes to handling dirty water, the dirty water pump is a must-have.Detail
Water Pumps: Solutions for Every NeedWhen it comes to handling dirty water, the dirty water pump is a must-have.Detail -
 Submersible Well Pumps: Reliable Water SolutionsWhen it comes to ensuring a reliable water supply, submersible well pumps are a top choice.Detail
Submersible Well Pumps: Reliable Water SolutionsWhen it comes to ensuring a reliable water supply, submersible well pumps are a top choice.Detail -
 Stainless Steel Water Pumps: Quality and DurabilityWhen it comes to choosing a water pump, the stainless steel water pump price is a crucial factor.Detail
Stainless Steel Water Pumps: Quality and DurabilityWhen it comes to choosing a water pump, the stainless steel water pump price is a crucial factor.Detail
