Nov . 21, 2024 21:22 Back to list
3 in submersible well pump
Understanding 3% in Submersible Well Pumps
Submersible well pumps have revolutionized the way we access groundwater. They are designed to be submerged in water and function by pushing water to the surface through a series of impellers. One crucial aspect often discussed in the context of submersible pumps is the efficiency parameter often referred to in percentages. When we mention 3% in submersible well pumps, it's essential to clarify what this percentage represents and how it impacts the pump's performance and overall functionality.
What Does 3% Mean?
The 3% figure typically refers to the maximum allowable variation in the pump's efficiency, operational performance, or energy consumption. In the context of submersible pumps, this variation can be related to several factors, including hydraulic design, motor efficiency, and installation conditions. Understanding this 3% threshold is vital for both manufacturers and consumers to ensure the pump operates efficiently and effectively over its lifespan.
Efficiency and Performance
Efficiency in submersible pumps is critical because it directly impacts operational costs and the longevity of the pump system. A pump operating at an efficiency level of 3% less than its maximum rated efficiency may imply that the motor is working harder than necessary, resulting in higher energy consumption and potential overheating. To put it in perspective, if a submersible pump is designed to operate optimally at 80% efficiency but is performing at 77%, the performance drop can lead to increased wear and tear and a shorter service life.
Importance of Proper Installation
3 in submersible well pump
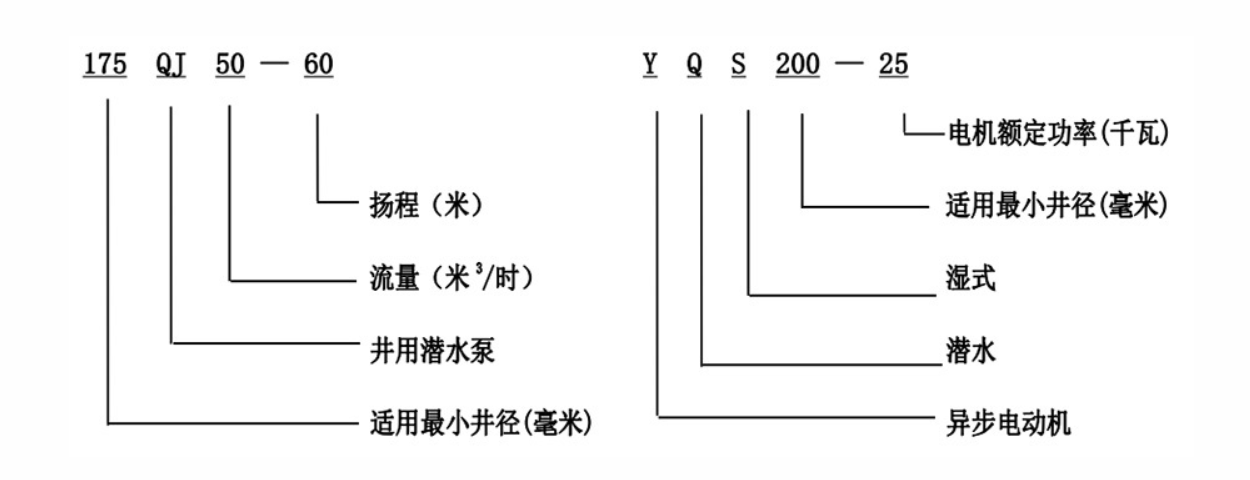
Proper installation can significantly impact the efficiency of a submersible well pump. Factors such as the depth of the well, the diameter of the pump, and the specific gravity of the fluid being pumped all play a role in ensuring that the pump can operate within its optimal range. If a pump is improperly installed, even the most efficient models may experience reductions in efficiency, sometimes falling within that concerning 3% range or even lower.
Maintenance Practices
Regular maintenance of submersible pumps is essential to keep performance steady within the desired efficiency parameters. Scheduled inspections, cleaning of the intake screens, and monitoring for unusual vibrations or noises can help prevent efficiency losses. Additionally, ensuring that the pump operates at the correct voltage and that each component is in good working order can aid in maintaining its high performance.
Choosing the Right Pump
When selecting a submersible well pump, buyers should consider the efficiency ratings and how they correlate with their specific needs. A pump with higher efficiency will typically cost more upfront but will provide significant savings in energy consumption over time. Therefore, understanding the implications of that 3% variance in efficiency becomes critical in making an informed purchasing decision.
Conclusion
In summary, the figure of 3% in the context of submersible well pumps serves as a crucial benchmark for ensuring optimal efficiency, performance, and cost-effectiveness. By maintaining proper installation practices, routine maintenance, and careful selection based on efficiency ratings, users can maximize the utility and lifespan of their submersible pumps. As groundwater resources become increasingly vital to address global water challenges, understanding the operational aspects of well pumps remains essential for sustainable management and access to this precious resource.
-
Submersible Well Pumps Buying Guide
NewsMay.14,2025
-
Submersible Sump, Dirty Water, Borehole Pumps Demystified
NewsMay.14,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pumps Superior Performance
NewsMay.14,2025
-
High Flow Submersible Well Pumps Essential Features
NewsMay.14,2025
-
Choosing the Best Stainless Well Pump
NewsMay.14,2025
-
A Comparison of Submersible Pumps Filled with Water and Oil
NewsMay.14,2025
-
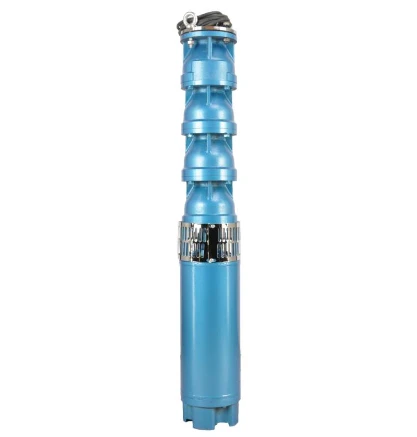 Submersible Well Pumps Buying GuideReliable access to clean water is fundamental for residential, agricultural, and commercial operations, making the selection of an appropriate well pump system one of the most important infrastructure decisions.Detail
Submersible Well Pumps Buying GuideReliable access to clean water is fundamental for residential, agricultural, and commercial operations, making the selection of an appropriate well pump system one of the most important infrastructure decisions.Detail -
 Submersible Sump, Dirty Water, Borehole Pumps DemystifiedThe world of water management has undergone a technological revolution, with advanced pumping systems now offering unprecedented efficiency and reliability across diverse applications.Detail
Submersible Sump, Dirty Water, Borehole Pumps DemystifiedThe world of water management has undergone a technological revolution, with advanced pumping systems now offering unprecedented efficiency and reliability across diverse applications.Detail -
 Stainless Steel Submersible Pumps Superior PerformanceModern water extraction and fluid handling systems demand equipment capable of withstanding harsh environments while maintaining peak efficiency.Detail
Stainless Steel Submersible Pumps Superior PerformanceModern water extraction and fluid handling systems demand equipment capable of withstanding harsh environments while maintaining peak efficiency.Detail
