Desemba . 03, 2024 21:11 Back to list
Illustration of a Submersible Pump System for Efficient Water Extraction
Understanding the Submersible Well Pump A Vital Resource for Water Extraction
Submersible well pumps are critical instruments used for extracting groundwater from deep wells. These pumps have a unique design that allows them to function efficiently underwater, making them ideal for a variety of applications, from residential water supply to agricultural irrigation and industrial uses. In this article, we will explore the working principles, components, benefits, and applications of submersible well pumps, emphasizing their importance in modern water management.
Working Principles
A submersible well pump operates by utilizing a series of stages that increase water pressure and facilitate its movement towards the surface. The pump is installed below the water level in a well, eliminating the need for suction mechanisms that can become inefficient in deep well applications. As the motor spins, impellers within the pump push water upward through the casing, which is then channeled to the surface through a discharge pipe.
One of the defining features of these pumps is their hermetically sealed design, which protects the motor from water exposure and potential damage. This feature not only enhances the pump's longevity but also reduces the risk of malfunction caused by debris or sediment in the water.
Components of a Submersible Well Pump
The key components of a submersible well pump include
1. Electric Motor The motor is typically water-cooled and mounted directly above the pump to maintain a compact design.
2. Pump Stages These consist of impellers and diffusers arranged in a series. The impellers are responsible for moving the water, while the diffusers help to convert the kinetic energy of the water into pressure.
3. Discharge Head This is the part where the water exits the pump and enters the discharge pipe. It often includes a check valve to prevent backflow.
4. Power Cable A specialized cable designed to power the pump while submerged, ensuring safe and efficient operation.
5. Drop Pipe This pipe connects the pump to the surface and serves as the conduit for water to travel upward.
6. Control System Modern submersible pumps often come equipped with control panels to manage the operation, monitor performance, and provide alerts for maintenance needs.
diagram of submersible well pump
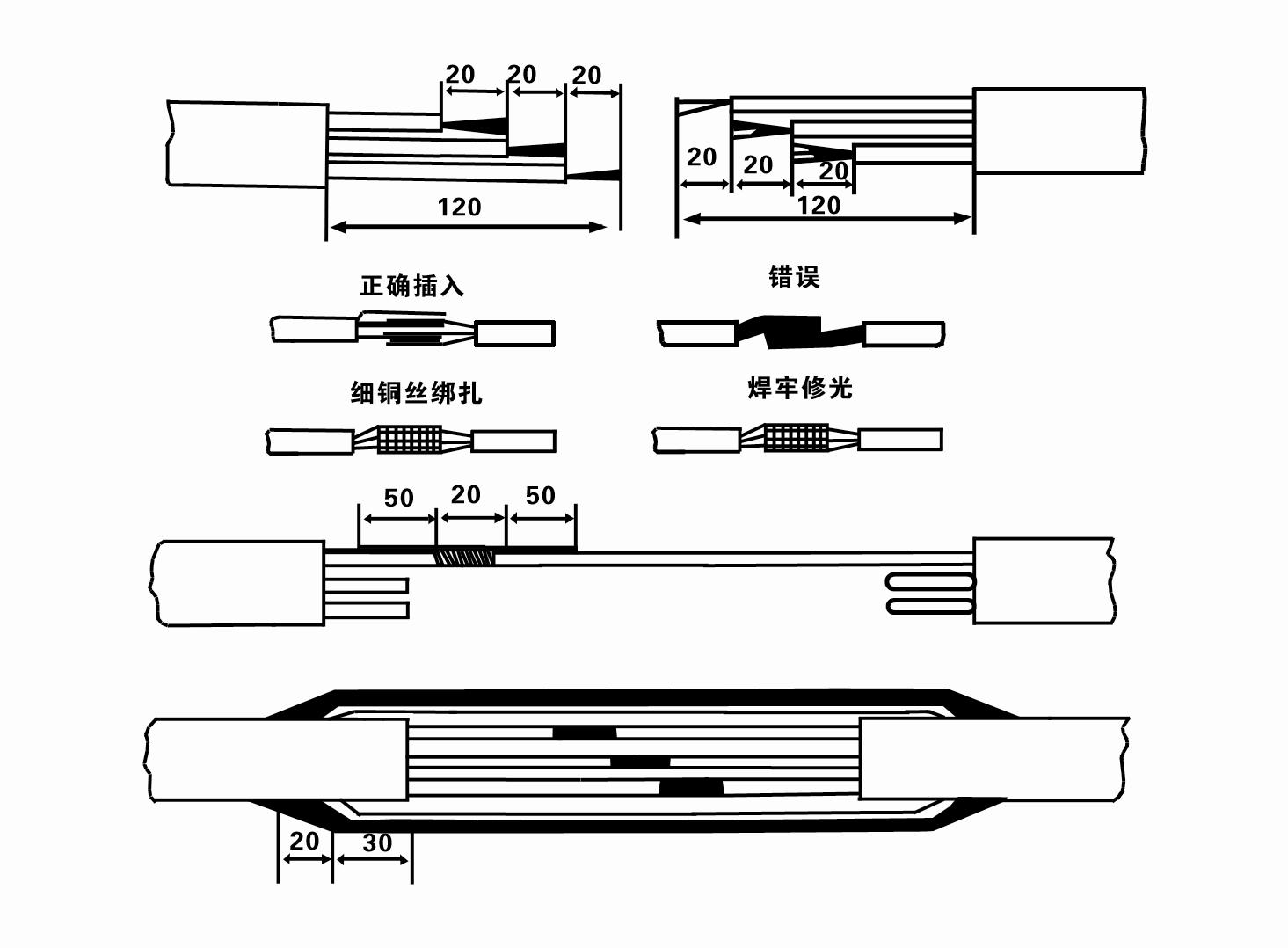
Benefits of Submersible Well Pumps
Submersible well pumps offer numerous advantages
- Efficiency By operating underwater, these pumps eliminate the need for suction, enhancing their efficiency in water extraction.
- Durability The robust design and materials used in submersible pumps ensure they can withstand harsh conditions and varying quality of groundwater.
- Space Saving Their design allows installation in tight spaces, making them suitable for urban and rural settings alike.
- Low Noise Operation Submersible pumps operate quietly, which is beneficial in residential areas or locations where noise pollution is a concern.
Applications
Submersible well pumps find applications in a range of settings
- Residential They are commonly used for supplying water to homes, particularly in areas where surface water sources are scarce.
- Agricultural Farmers use these pumps for irrigation, ensuring crops receive the necessary water supply for healthy growth, even in arid conditions.
- Industrial Industries rely on submersible pumps for various processes, including cooling, water supply for manufacturing, and even dewatering construction sites.
In conclusion, submersible well pumps are essential tools for water extraction that support various sectors, from homes to agriculture and industry. Understanding their functioning and components can help users maintain these pumps effectively, ensuring a continuous supply of fresh water, which is vital in today’s world. As we face increasing challenges related to water scarcity, the role of submersible well pumps in sustainable water management becomes ever more significant.
-
Submersible Well Pumps Buying Guide
NewsMay.14,2025
-
Submersible Sump, Dirty Water, Borehole Pumps Demystified
NewsMay.14,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pumps Superior Performance
NewsMay.14,2025
-
High Flow Submersible Well Pumps Essential Features
NewsMay.14,2025
-
Choosing the Best Stainless Well Pump
NewsMay.14,2025
-
A Comparison of Submersible Pumps Filled with Water and Oil
NewsMay.14,2025
-
 Submersible Well Pumps Buying GuideReliable access to clean water is fundamental for residential, agricultural, and commercial operations, making the selection of an appropriate well pump system one of the most important infrastructure decisions.Detail
Submersible Well Pumps Buying GuideReliable access to clean water is fundamental for residential, agricultural, and commercial operations, making the selection of an appropriate well pump system one of the most important infrastructure decisions.Detail -
 Submersible Sump, Dirty Water, Borehole Pumps DemystifiedThe world of water management has undergone a technological revolution, with advanced pumping systems now offering unprecedented efficiency and reliability across diverse applications.Detail
Submersible Sump, Dirty Water, Borehole Pumps DemystifiedThe world of water management has undergone a technological revolution, with advanced pumping systems now offering unprecedented efficiency and reliability across diverse applications.Detail -
 Stainless Steel Submersible Pumps Superior PerformanceModern water extraction and fluid handling systems demand equipment capable of withstanding harsh environments while maintaining peak efficiency.Detail
Stainless Steel Submersible Pumps Superior PerformanceModern water extraction and fluid handling systems demand equipment capable of withstanding harsh environments while maintaining peak efficiency.Detail
