Peb . 10, 2025 23:13 Back to list
175QJ Deep Well Submersible Pump
Exploring the complexities of submersible water well pump diagrams provides valuable insights for homeowners, engineers, and technicians aiming to maximize the efficiency and lifecycle of water well systems. Expertise in understanding these diagrams is crucial for the effective management of water resources and addressing the unique challenges posed by groundwater extraction.
A check valve is strategically positioned in the diagram above the pump mechanism. This valve serves to prevent backflow into the pump, a critical function in safeguarding against potential water hammer effects which could otherwise damage the system. By explicitly representing the check valve in the diagram, users and technicians can appreciate its preventive role and ensure it is routinely inspected for optimal performance. The power cable is depicted prominently, often sheathed for protection against abrasions and chemical exposure within the well environment. Accurate interpretation of this segment in the diagram is crucial to maintaining good electrical connectivity and avoiding potentially hazardous situations. Moreover, understanding the role of the pressure switch, shown in the diagram, is fundamental. It automates the pump's operation based on water level and pressure, initiating and halting the motor as required. By emphasizing this automated feature, the diagram reinforces the importance of precision in setting pressure levels to avoid excessive wear on the pump components. The inclusion of control box details within the diagram provides an additional layer of operation management by housing the electrical circuits that regulate the motor's running cycle. By ensuring these controls are correctly depicted, the diagram underpins the systematic integration of all electrical and mechanical parts of the pump. In sum, the submersible water well pump diagram serves as an authoritative guide for stakeholders involved in water management. By mastering this diagram, one not only gains an in-depth understanding of the pump's mechanical and electrical synergy but also achieves a heightened level of trustworthiness in maintaining well-balanced groundwater extraction systems. Emphasizing the precision and expertise captured through such diagrams enhances both the reliability and sustainability of submersible well applications, safeguarding vital water resources for generations to come.

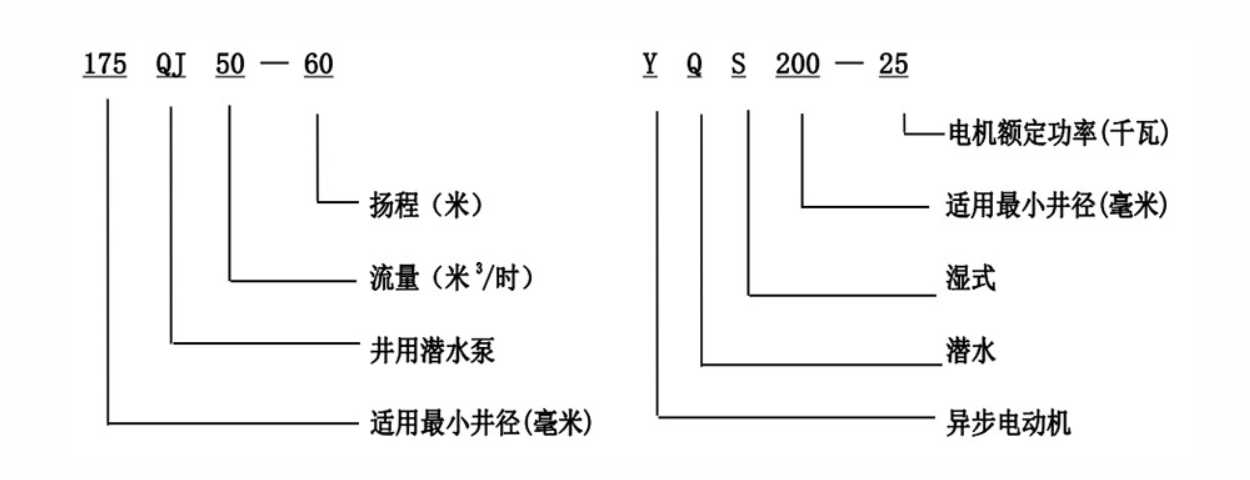
A check valve is strategically positioned in the diagram above the pump mechanism. This valve serves to prevent backflow into the pump, a critical function in safeguarding against potential water hammer effects which could otherwise damage the system. By explicitly representing the check valve in the diagram, users and technicians can appreciate its preventive role and ensure it is routinely inspected for optimal performance. The power cable is depicted prominently, often sheathed for protection against abrasions and chemical exposure within the well environment. Accurate interpretation of this segment in the diagram is crucial to maintaining good electrical connectivity and avoiding potentially hazardous situations. Moreover, understanding the role of the pressure switch, shown in the diagram, is fundamental. It automates the pump's operation based on water level and pressure, initiating and halting the motor as required. By emphasizing this automated feature, the diagram reinforces the importance of precision in setting pressure levels to avoid excessive wear on the pump components. The inclusion of control box details within the diagram provides an additional layer of operation management by housing the electrical circuits that regulate the motor's running cycle. By ensuring these controls are correctly depicted, the diagram underpins the systematic integration of all electrical and mechanical parts of the pump. In sum, the submersible water well pump diagram serves as an authoritative guide for stakeholders involved in water management. By mastering this diagram, one not only gains an in-depth understanding of the pump's mechanical and electrical synergy but also achieves a heightened level of trustworthiness in maintaining well-balanced groundwater extraction systems. Emphasizing the precision and expertise captured through such diagrams enhances both the reliability and sustainability of submersible well applications, safeguarding vital water resources for generations to come.
Latest news
-
submersible-sump-pump-auto-drainage-for-crawlspaces
NewsAug.22,2025
-
solar-powered-stainless-steel-submersible-well-pump-setup
NewsAug.22,2025
-
stainless-steel-well-pump-flow-rate-optimization
NewsAug.22,2025
-
water-filled-submersible-pump-fish-farm-oxygenation
NewsAug.22,2025
-
submersible-pump-in-aquaculture-and-fish-farming
NewsAug.22,2025
-
deep-well-submersible-pump-for-drought-areas
NewsAug.22,2025
-
 submersible-sump-pump-auto-drainage-for-crawlspacesCrawlspaces, those narrow areas beneath homes, are prone to water accumulation due to leaks, groundwDetail
submersible-sump-pump-auto-drainage-for-crawlspacesCrawlspaces, those narrow areas beneath homes, are prone to water accumulation due to leaks, groundwDetail -
 solar-powered-stainless-steel-submersible-well-pump-setupHarnessing solar energy to power stainless steel submersible well pumps is a sustainable and coDetail
solar-powered-stainless-steel-submersible-well-pump-setupHarnessing solar energy to power stainless steel submersible well pumps is a sustainable and coDetail -
 stainless-steel-well-pump-flow-rate-optimizationIn various applications like agriculture, domestic water supply, and industrial use, the flow rate oDetail
stainless-steel-well-pump-flow-rate-optimizationIn various applications like agriculture, domestic water supply, and industrial use, the flow rate oDetail
