Jul . 29, 2024 20:49 Back to list
Guidelines for Proper Installation of Submersible Pumps in Deep Well Water Systems
Understanding Deep Well Submersible Pump Installation A Comprehensive Guide
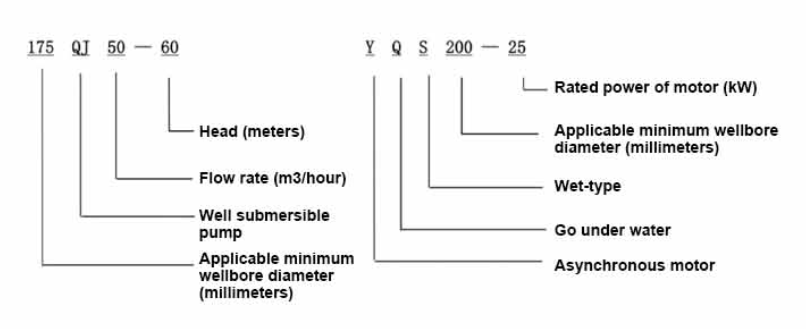
Deep well submersible pumps play a vital role in water extraction and are widely used for various applications, including agricultural irrigation, residential water supply, and industrial operations. The installation of these pumps requires a solid understanding of their components and proper techniques to ensure optimal performance. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the installation process for a deep well submersible pump, illustrated by a general installation diagram.
Components of a Deep Well Submersible Pump
Before diving into the installation process, it is essential to understand the various components involved in a deep well submersible pump system. Major components include
1. Pump Body The main unit that contains the motor and pump stages and is submerged in the well. 2. Motor Typically an electric motor designed to operate underwater. 3. Discharge Head The part of the pump that is located above ground and connects the pump to the piping system. 4. Column Pipe The vertical pipe that houses the pump and allows water to flow to the surface. 5. Seal and Check Valve To prevent backflow and protect the pump from contaminants.
Installation Process
The installation of a deep well submersible pump can be illustrated in several key steps
1. Site Preparation Ensure that the well is clean and free of debris. Determine the depth of the well to select the appropriately sized pump and ensure that it is suitable for the specific water needs.
2. Pump Selection Based on the water demand and anticipated flow rates, select a pump that offers the necessary horsepower and total dynamic head (TDH). Consult the manufacturer’s specifications for recommendations.
3. Lowering the Pump Using a crane or winch, carefully lower the pump into the well. It is critical to do this slowly to avoid damaging the pump or well casing. Make sure the pump is aligned with the well casing and that the column pipe is straight.
deep well submersible pump installation diagram
4. Connecting the Discharge Pipe Once the pump is in place, connect the discharge head to the discharge pipe. This connection must be secure to prevent leaks. It is advisable to use Teflon tape on the threads of the fittings to ensure a tight seal.
5. Electrical Connections Make the necessary electrical connections to power the pump. Be sure to follow local electrical codes and manufacturer guidelines. A dedicated circuit with a properly sized breaker is recommended for safe operation.
6. Testing the System After completing the installation, conduct tests to ensure that the system operates effectively. Monitor the flow rate, pressure, and electrical performance. Listen for unusual noises that may indicate issues within the pump.
7. Installation of Control Panel Install a control panel above ground to manage the pump operations, including a pressure switch or float switch that controls the pump based on water levels.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
After installation, regular maintenance is crucial for optimal performance. Schedule annual inspections to check for wear and tear on the pump components, inspect electrical connections, and ensure that water quality remains high.
Common issues include pump failure, low flow rates, or unusual noises. Troubleshooting may involve checking the motor, inspecting the discharge pipe for blockages, or assessing the electrical connections.
Conclusion
Installing a deep well submersible pump is a complex yet rewarding task that can efficiently provide water for various needs. By following a systematic installation process and understanding the components involved, users can ensure longevity and reliability in their water extraction efforts. Proper maintenance and troubleshooting will further enhance the pump's performance, making it an invaluable asset for many applications.
-
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater World
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape Ecology
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main Force
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Stainless Steel Submersible Pump: An Efficient and Versatile Tool for Underwater Operations
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Well Submersible Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Deep Water Well Pump: An Efficient 'Sucker' of Groundwater Sources
NewsJul.01,2025
-
 Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail
Submersible Water Pump: The Efficient 'Power Pioneer' of the Underwater WorldIn the field of hydraulic equipment, the Submersible Water Pump has become the core equipment for underwater operations and water resource transportation due to its unique design and excellent performance.Detail -
 Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail
Submersible Pond Pump: The Hidden Guardian of Water Landscape EcologyIn courtyard landscapes, ecological ponds, and even small-scale water conservancy projects, there is a silent yet indispensable equipment - the Submersible Pond Pump.Detail -
 Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
Stainless Well Pump: A Reliable and Durable Pumping Main ForceIn the field of water resource transportation, Stainless Well Pump has become the core equipment for various pumping scenarios with its excellent performance and reliable quality.Detail
