Jan . 24, 2025 01:27 Back to list
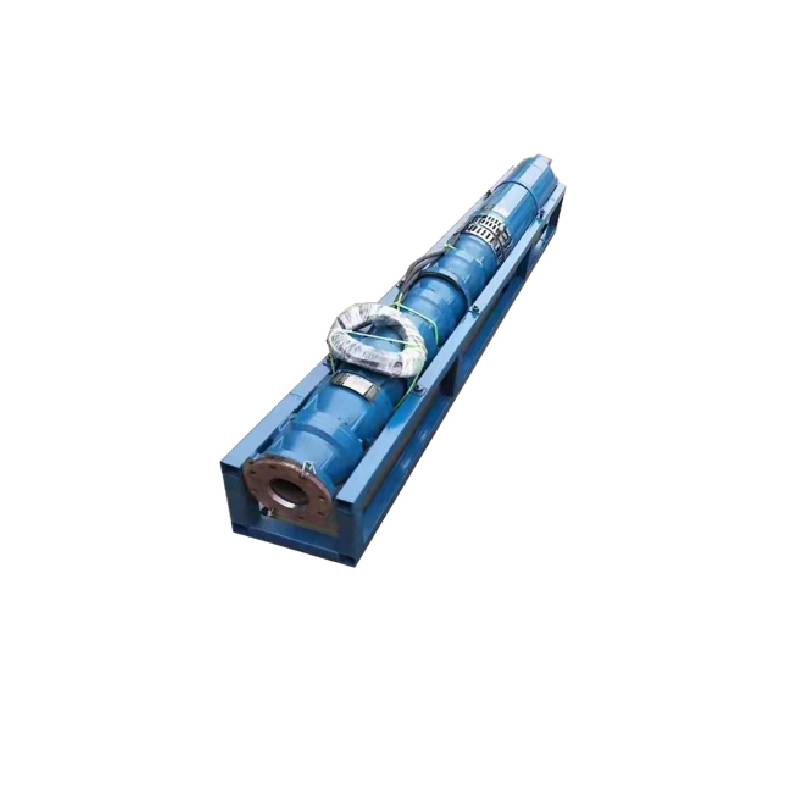
industrial submersible pump
Industrial submersible pumps are a revolution in the world of fluid management, offering unparalleled efficiency and reliability in demanding environments. These robust pieces of equipment are integral to operations across various industries, including mining, construction, and wastewater management. Their profound impact stems from a unique set of characteristics that make them superior to traditional pumping systems.
In terms of authoritativeness, industry leaders like Grundfos, Sulzer, and Xylem are at the forefront, continuously innovating their product lines to meet evolving industrial demands. Their extensive experience in pump technology and engineering positions them as trusted advisors to industries across the globe. By integrating smart technologies and IoT interfaces, these companies provide users with real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance capabilities. This integration helps prevent unscheduled downtime by allowing operators to identify and address potential issues before they escalate. From an experiential perspective, the adoption of industrial submersible pumps has been transformative. Users appreciate the reduced noise levels and minimal footprint these pumps offer compared to their above-ground counterparts. Moreover, the ease of installation and the ability to operate in confined spaces where traditional pumps would fail expands their applicability across diverse settings. Whether in urban wastewater plants dealing with heavy rainfall or mining operations managing groundwater ingress, these pumps deliver unmatched performance. Furthermore, the energy efficiency of industrial submersible pumps is a significant benefit, aligning with contemporary sustainability goals. Their design ensures optimal load management and power consumption, allowing companies to reduce their carbon footprint while maintaining operational efficiency. As energy costs continue to rise, this feature is increasingly valuable, offering both environmental and economic advantages. In conclusion, industrial submersible pumps represent a blend of advanced engineering, superior reliability, and operational flexibility. Their ability to handle complex fluid management tasks while ensuring user convenience and cost savings makes them an indispensable tool in modern industry. By prioritizing the Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness—dubbed the E-E-A-T criteria—of these pumps, businesses can confidently invest in this technology, assured of its capability to meet both current and future demands.

In terms of authoritativeness, industry leaders like Grundfos, Sulzer, and Xylem are at the forefront, continuously innovating their product lines to meet evolving industrial demands. Their extensive experience in pump technology and engineering positions them as trusted advisors to industries across the globe. By integrating smart technologies and IoT interfaces, these companies provide users with real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance capabilities. This integration helps prevent unscheduled downtime by allowing operators to identify and address potential issues before they escalate. From an experiential perspective, the adoption of industrial submersible pumps has been transformative. Users appreciate the reduced noise levels and minimal footprint these pumps offer compared to their above-ground counterparts. Moreover, the ease of installation and the ability to operate in confined spaces where traditional pumps would fail expands their applicability across diverse settings. Whether in urban wastewater plants dealing with heavy rainfall or mining operations managing groundwater ingress, these pumps deliver unmatched performance. Furthermore, the energy efficiency of industrial submersible pumps is a significant benefit, aligning with contemporary sustainability goals. Their design ensures optimal load management and power consumption, allowing companies to reduce their carbon footprint while maintaining operational efficiency. As energy costs continue to rise, this feature is increasingly valuable, offering both environmental and economic advantages. In conclusion, industrial submersible pumps represent a blend of advanced engineering, superior reliability, and operational flexibility. Their ability to handle complex fluid management tasks while ensuring user convenience and cost savings makes them an indispensable tool in modern industry. By prioritizing the Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness—dubbed the E-E-A-T criteria—of these pumps, businesses can confidently invest in this technology, assured of its capability to meet both current and future demands.
Latest news
-
Water Pumps: Solutions for Every Need
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Submersible Well Pumps: Reliable Water Solutions
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Stainless Steel Water Pumps: Quality and Durability
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Powerful Water Pumps: Your Solution for Efficient Water Management
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Oil vs Water Filled Submersible Pumps: Which is Better?
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Deep Well Pumps: Power and Reliability
NewsJul.30,2025
-
 Water Pumps: Solutions for Every NeedWhen it comes to handling dirty water, the dirty water pump is a must-have.Detail
Water Pumps: Solutions for Every NeedWhen it comes to handling dirty water, the dirty water pump is a must-have.Detail -
 Submersible Well Pumps: Reliable Water SolutionsWhen it comes to ensuring a reliable water supply, submersible well pumps are a top choice.Detail
Submersible Well Pumps: Reliable Water SolutionsWhen it comes to ensuring a reliable water supply, submersible well pumps are a top choice.Detail -
 Stainless Steel Water Pumps: Quality and DurabilityWhen it comes to choosing a water pump, the stainless steel water pump price is a crucial factor.Detail
Stainless Steel Water Pumps: Quality and DurabilityWhen it comes to choosing a water pump, the stainless steel water pump price is a crucial factor.Detail
